Rheostat functional outcomes occur when substitutions are introduced at nonconserved positions that diverge with speciation
- PMID: 34076313
- PMCID: PMC8376419
- DOI: 10.1002/pro.4136
Rheostat functional outcomes occur when substitutions are introduced at nonconserved positions that diverge with speciation
Abstract
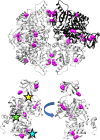
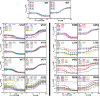
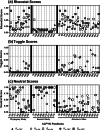
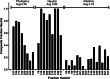
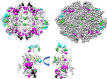
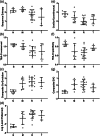
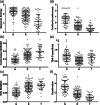
When amino acids vary during evolution, the outcome can be functionally neutral or biologically-important. We previously found that substituting a subset of nonconserved positions, "rheostat" positions, can have surprising effects on protein function. Since changes at rheostat positions can facilitate functional evolution or cause disease, more examples are needed to understand their unique biophysical characteristics. Here, we explored whether "phylogenetic" patterns of change in multiple sequence alignments (such as positions with subfamily specific conservation) predict the locations of functional rheostat positions. To that end, we experimentally tested eight phylogenetic positions in human liver pyruvate kinase (hLPYK), using 10-15 substitutions per position and biochemical assays that yielded five functional parameters. Five positions were strongly rheostatic and three were non-neutral. To test the corollary that positions with low phylogenetic scores were not rheostat positions, we combined these phylogenetic positions with previously-identified hLPYK rheostat, "toggle" (most substitution abolished function), and "neutral" (all substitutions were like wild-type) positions. Despite representing 428 variants, this set of 33 positions was poorly statistically powered. Thus, we turned to the in vivo phenotypic dataset for E. coli lactose repressor protein (LacI), which comprised 12-13 substitutions at 329 positions and could be used to identify rheostat, toggle, and neutral positions. Combined hLPYK and LacI results show that positions with strong phylogenetic patterns of change are more likely to exhibit rheostat substitution outcomes than neutral or toggle outcomes. Furthermore, phylogenetic patterns were more successful at identifying rheostat positions than were co-evolutionary or eigenvector centrality measures of evolutionary change.
Keywords: evolution; lactose repressor protein; phylogeny; pyruvate kinase; rheostat positions.
© 2021 The Protein Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rheostats, toggles, and neutrals, Oh my! A new framework for understanding how amino acid changes modulate protein function.J Biol Chem. 2024 Mar;300(3):105736. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105736. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38336297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamics-based protein network features accurately discriminate neutral and rheostat positions.Biophys J. 2024 Oct 15;123(20):3612-3626. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.09.013. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 39277794
-
Identification of biochemically neutral positions in liver pyruvate kinase.Proteins. 2020 Oct;88(10):1340-1350. doi: 10.1002/prot.25953. Epub 2020 Jun 27. Proteins. 2020. PMID: 32449829 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the functional roles of nonconserved sequence positions in homologous transcription repressors: implications for sequence/function analyses.J Mol Biol. 2010 Jan 29;395(4):785-802. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.10.001. Epub 2009 Oct 8. J Mol Biol. 2010. PMID: 19818797 Free PMC article.
-
Substitutions at Nonconserved Rheostat Positions Modulate Function by Rewiring Long-Range, Dynamic Interactions.Mol Biol Evol. 2021 Jan 4;38(1):201-214. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msaa202. Mol Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 32780837 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Discovering interrelated natural mutations of efflux pump KmrA from Klebsiella pneumoniae that confer increased multidrug resistance.Protein Sci. 2022 Jun;31(6):e4323. doi: 10.1002/pro.4323. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 35634772 Free PMC article.
-
The intrinsically disordered transcriptional activation domain of CIITA is functionally tuneable by single substitutions: An exception or a new paradigm?Protein Sci. 2024 Feb;33(2):e4863. doi: 10.1002/pro.4863. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38073129 Free PMC article.
-
Rheostats, toggles, and neutrals, Oh my! A new framework for understanding how amino acid changes modulate protein function.J Biol Chem. 2024 Mar;300(3):105736. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.105736. Epub 2024 Feb 8. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38336297 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rheostatic contributions to protein stability can obscure a position's functional role.Protein Sci. 2024 Jul;33(7):e5075. doi: 10.1002/pro.5075. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38895978
-
Dynamics-based protein network features accurately discriminate neutral and rheostat positions.Biophys J. 2024 Oct 15;123(20):3612-3626. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.09.013. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 39277794
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

