Chronicles of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Targeting EGFR C797S Containing Triple Mutations
- PMID: 34074804
- PMCID: PMC8724843
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2021.047
Chronicles of EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Targeting EGFR C797S Containing Triple Mutations
Abstract
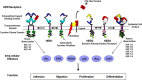
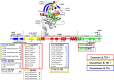
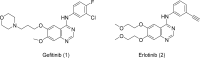
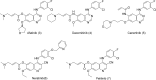
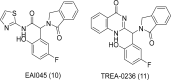
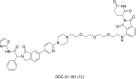
Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is a receptor tyrosine kinase widely expressed in many cancers such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, and head and neck cancer. Mutations such as L858R in exon 21, exon 19 truncation (Del19), exon 20 insertions, and others are responsible for aberrant activation of EGFR in NSCLC. First-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) such as gefitinib and erlotinib have clinical benefits for EGFR-sensitive (L858R and Del19) NSCLC patients. However, after 10-12 months of treatment with these inhibitors, a secondary T790M mutation at the gatekeeper position in the kinase domain of EGFR was identified, which limited the clinical benefits. Second-generation EGFR irreversible inhibitors (afatinib and dacomitinib) were developed to overcome this T790M mutation. However, their lack of selectivity toward wild-type EGFR compromised their clinical benefits due to serious adverse events. Recently developed third-generation irreversible EGFR TKIs (osimertinib and lazertinib) are selective toward driving mutations and the T790M mutation, while sparing wildtype EGFR activity. The latest studies have concluded that their efficacy was also compromised by additional acquired mutations, including C797S, the key residue cysteine that forms covalent bonds with irreversible inhibitors. Because second- and thirdgeneration EGFR TKIs are irreversible inhibitors, they are not effective against C797S containing EGFR triple mutations (Del19/T790M/C797S and L858R/T790M/C797S). Therefore, there is an urgent unmet medical need to develop next-generation EGFR TKIs that selectively inhibit EGFR triple mutations via a non-irreversible mechanism.
Keywords: Acquired resistance; C797S; EGFR; NSCLC; T790M; TKIs.
Figures
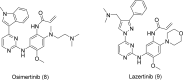
Similar articles
-
Insights into fourth generation selective inhibitors of (C797S) EGFR mutation combating non-small cell lung cancer resistance: a critical review.RSC Adv. 2023 Jun 21;13(27):18825-18853. doi: 10.1039/d3ra02347h. eCollection 2023 Jun 15. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37350862 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Response to Brigatinib Targeted Therapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Exon 19 Deletion, T790M, and cis-C797S Triple Mutations: A Case Report.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 29;24(1):602. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010602. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36614045 Free PMC article.
-
Audit of Molecular Mechanisms of Primary and Secondary Resistance to Various Generations of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Known Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Mutant Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients in a Tertiary Centre.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022 Nov;34(11):e451-e462. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2022.06.003. Epub 2022 Jul 7. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2022. PMID: 35810049
-
Next-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors to overcome C797S mutation in non-small cell lung cancer (2019-2024).RSC Med Chem. 2024 Aug 30;15(10):3371-94. doi: 10.1039/d4md00384e. Online ahead of print. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 39246743 Review.
-
Characterization of EGFR T790M, L792F, and C797S Mutations as Mechanisms of Acquired Resistance to Afatinib in Lung Cancer.Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Feb;16(2):357-364. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-16-0407. Epub 2016 Dec 2. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017. PMID: 27913578
Cited by
-
Molecular targeted therapy for anticancer treatment.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Oct;54(10):1670-1694. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00864-3. Epub 2022 Oct 12. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36224343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling Extremely Damaging IRAK4 Variants and Their Potential Implications for IRAK4 Inhibitor Efficacy.J Pers Med. 2023 Nov 26;13(12):1648. doi: 10.3390/jpm13121648. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 38138875 Free PMC article.
-
Effective clinical response of lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR 19Del/T790M/in cis-C797S osimertinib to osimertinib and gefitinib combination therapy.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023 Aug 1;13(8):5362-5368. doi: 10.21037/qims-22-1269. Epub 2023 May 11. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2023. PMID: 37581042 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
EGFR trafficking: effect of dimerization, dynamics, and mutation.Front Oncol. 2023 Sep 11;13:1258371. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1258371. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37752992 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insights into fourth generation selective inhibitors of (C797S) EGFR mutation combating non-small cell lung cancer resistance: a critical review.RSC Adv. 2023 Jun 21;13(27):18825-18853. doi: 10.1039/d3ra02347h. eCollection 2023 Jun 15. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37350862 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akazawa Y., Saito Y., Yoshikawa T., Saito K., Nosaka K., Shimomura M., Mizuno S., Nakamoto Y., Nakatsura T. Efficacy of immunotherapy targeting the neoantigen derived from epidermal growth factor receptor T790M/C797S mutation in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2020;111:2736–2746. doi: 10.1111/cas.14451. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

