Strong Inhibitory Activity and Action Modes of Synthetic Maslinic Acid Derivative on Highly Pathogenic Coronaviruses: COVID-19 Drug Candidate
- PMID: 34069460
- PMCID: PMC8159111
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens10050623
Strong Inhibitory Activity and Action Modes of Synthetic Maslinic Acid Derivative on Highly Pathogenic Coronaviruses: COVID-19 Drug Candidate
Abstract
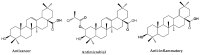
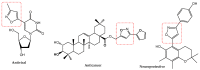
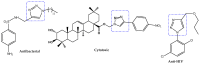
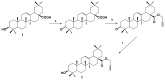
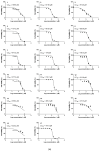
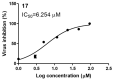
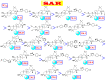
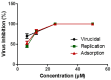
In late December 2019, a novel coronavirus, namely severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), escaped the animal-human interface and emerged as an ongoing global pandemic with severe flu-like illness, commonly known as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). In this study, a molecular docking study was carried out for seventeen (17) structural analogues prepared from natural maslinic and oleanolic acids, screened against SARS-CoV-2 main protease. Furthermore, we experimentally validated the virtual data by measuring the half-maximal cytotoxic and inhibitory concentrations of each compound. Interestingly, the chlorinated isoxazole linked maslinic acid (compound 17) showed promising antiviral activity at micromolar non-toxic concentrations. Thoughtfully, we showed that compound 17 mainly impairs the viral replication of SARS-CoV-2. Furthermore, a very promising SAR study for the examined compounds was concluded, which could be used by medicinal chemists in the near future for the design and synthesis of potential anti-SARS-CoV-2 candidates. Our results could be very promising for performing further additional in vitro and in vivo studies on the tested compound (17) before further licensing for COVID-19 treatment.
Keywords: MERS-CoV; SAR; SARS-CoV-2; maslinic acid; molecular docking; oleanolic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Current status of antivirals and druggable targets of SARS CoV-2 and other human pathogenic coronaviruses.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100721. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33132205 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery and mechanism of action of Thonzonium bromide from an FDA-approved drug library with potent and broad-spectrum inhibitory activity against main proteases of human coronaviruses.Bioorg Chem. 2023 Jan;130:106264. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2022.106264. Epub 2022 Nov 9. Bioorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 36395603 Free PMC article.
-
Establishing an Analogue Based In Silico Pipeline in the Pursuit of Novel Inhibitory Scaffolds against the SARS Coronavirus 2 Papain-Like Protease.Molecules. 2021 Feb 20;26(4):1134. doi: 10.3390/molecules26041134. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33672721 Free PMC article.
-
Current Strategies of Antiviral Drug Discovery for COVID-19.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 May 13;8:671263. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.671263. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34055887 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potent 3CLpro inhibitors effective against SARS-CoV-2 and MERS-CoV in animal models by therapeutic treatment.mBio. 2024 Feb 14;15(2):e0287823. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02878-23. Epub 2023 Dec 21. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38126789 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Current Research on Infectious Diseases of Domestic Animals from a One Health Perspective.Pathogens. 2023 May 17;12(5):724. doi: 10.3390/pathogens12050724. Pathogens. 2023. PMID: 37242394 Free PMC article.
-
Investigating the structure-activity relationship of marine natural polyketides as promising SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors.RSC Adv. 2021 Sep 22;11(50):31339-31363. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05817g. eCollection 2021 Sep 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35496831 Free PMC article.
-
Design, Synthesis, Biological Evaluation, 2D-QSAR Modeling, and Molecular Docking Studies of Novel 1H-3-Indolyl Derivatives as Significant Antioxidants.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 27;22(19):10396. doi: 10.3390/ijms221910396. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34638734 Free PMC article.
-
In Silico and In Vitro Studies for Benzimidazole Anthelmintics Repurposing as VEGFR-2 Antagonists: Novel Mebendazole-Loaded Mixed Micelles with Enhanced Dissolution and Anticancer Activity.ACS Omega. 2021 Dec 22;7(1):875-899. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c05519. eCollection 2022 Jan 11. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 35036753 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advances in COVID-19-induced liver injury: causes, diagnosis, and management.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Oct;32(5):2649-2680. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01535-7. Epub 2024 Aug 10. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39126569 Review.
References
-
- Kumar S., Singh R., Kumari N., Karmakar S., Behera M., Siddiqui A.J., Rajput V.D., Minkina T., Bauddh K., Kumar N. Current understanding of the influence of environmental factors on sars-cov-2 transmission, persistence, and infectivity. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021;28:6267–6288. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-12165-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Mostafa A., Kandeil A., Elshaier Y.A.M.M., Kutkat O., Moatasim Y., Rashad A.A., Shehata M., Gomaa M.R., Mahrous N., Mahmoud S.H., et al. Fda-approved drugs with potent in vitro antiviral activity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. Pharmaceuticals. 2020;13:443. doi: 10.3390/ph13120443. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Surti M., Patel M., Adnan M., Moin A., Ashraf S.A., Siddiqui A.J., Snoussi M., Deshpande S., Reddy M.N. Ilimaquinone (marine sponge metabolite) as a novel inhibitor of sars-cov-2 key target proteins in comparison with suggested covid-19 drugs: Designing, docking and molecular dynamics simulation study. RSC Adv. 2020;10:37707–37720. doi: 10.1039/D0RA06379G. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

