Antimicrobial Activity of Selected Essential Oils against Selected Pathogenic Bacteria: In Vitro Study
- PMID: 34066788
- PMCID: PMC8151751
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics10050546
Antimicrobial Activity of Selected Essential Oils against Selected Pathogenic Bacteria: In Vitro Study
Abstract
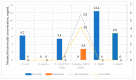
The worldwide problem of infectious diseases has appeared in recent years, and antimicrobial agents are crucial in reducing disease emergence. Nevertheless, the development and distribution of multidrug-resistant (MDR) strains in pathogenic bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, Salmonella Typhi and Citrobacter koseri, has become a major society health hazard. Essential oils could serve as a promising tool as a natural drug in fighting the problem with these bacteria. The current study aimed to investigate the antimicrobial effectiveness of tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia (Maiden and Betche) Cheel), rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis L.), eucalyptus (Eucalyptus obliqua L'Hér.), and lavender (Lavandula angustifolia Mill) essential oils. The antimicrobial properties of essential oils were screened against four pathogenic bacteria, E. coli, S. aureus, S. Tyhpi, and C. koseri, and two reference bacterial strains, while for the testing, the agar well diffusion method was used. Gas chromatography (GC) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometric (GC-MSD) analyses were performed on essential oils. The obtained results showed that M. alternifolia essential oil is the richest in terpinen-4-ol, R. officinalis and E. oblique essential oils in 1,8-cineole, and L. angustifolia essential oil in α-terpinyl acetate. In addition, the main bioactive compounds present in the essential oil of tea tree are rich in α-pinene (18.38%), limonene (7.55%) and γ-terpinene (14.01%). The essential oil of rosemary is rich in α-pinene (8.38%) and limonene (11.86%); eucalyptus essential oil has significant concentrations of α-pinene (12.60%), p-cymene (3.24%), limonene (3.87%), and γ-terpinene (7.37%), while the essential oil of lavender is rich in linalool (10.71%), linalool acetate (9.60%), α-terpinyl acetate (10.93%), and carbitol (13.05%) bioactive compounds, respectively. The obtained results from the in vitro study revealed that most of the essential oils exhibited antimicrobial properties. Among the tested essential oils, tea tree was discovered to demonstrate the strongest antimicrobial activity. The recorded MIC of S. Typhi was 6.2 mg/mL, 3.4 mg/mL of C. koseri, 3.1 mg/mL of E. coli, and 2.7 mg/mL of E. coli ATCC 25922, compared to M. alternifolia. Similarly, only S. aureus ATCC 25923 showed antimicrobial activity towards R. officinalis (1.4 mg/mL), E. oblique (2.9 mg/mL), and L. angustifolia (2.1 mg/mL). Based on the obtained results, it is possible to conclude that tea tree essential oil might be used as an ecological antimicrobial in treating infectious diseases caused by the tested pathogens.
Keywords: C. koseri; E. coli; S. Thypi; S. aureus; antibiotic resistance; essential oils; microbes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antimicrobial synergism and cytotoxic properties of Citrus limon L., Piper nigrum L. and Melaleuca alternifolia (Maiden and Betche) Cheel essential oils.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017 Nov;69(11):1606-1614. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12792. Epub 2017 Aug 17. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28815601
-
HPTLC Analysis and Chemical Composition of Selected Melaleuca Essential Oils.Molecules. 2023 May 6;28(9):3925. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093925. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175338 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial capabilities of non-spermicidal concentrations of tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia) and rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis) essential oils on the liquid phase of refrigerated swine seminal doses.Res Vet Sci. 2019 Dec;127:76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.rvsc.2019.10.014. Epub 2019 Oct 25. Res Vet Sci. 2019. PMID: 31678456
-
River Tea Tree Oil: Composition, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities, and Potential Applications in Agriculture.Plants (Basel). 2021 Oct 4;10(10):2105. doi: 10.3390/plants10102105. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plants of the Melaleuca Genus as Antimicrobial Agents: From Farm to Pharmacy.Phytother Res. 2017 Oct;31(10):1475-1494. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5880. Epub 2017 Aug 7. Phytother Res. 2017. PMID: 28782167 Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the Broad Antimicrobial Activity of Melaleuca alternifolia Tea Tree Oil by Combining Experimental and Computational Investigations.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 4;24(15):12432. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512432. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569803 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant-Rich Natural Raw Materials in the Prevention and Treatment of Selected Oral Cavity and Periodontal Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 21;10(11):1848. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111848. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829719 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine and its Active Ingredients on Drug-Resistant Bacteria.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 2;13:837907. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.837907. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35721131 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimization of Veterinary Antimicrobial Treatment in Companion and Food Animals.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Aug 22;11(8):1137. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11081137. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36010005 Free PMC article.
-
Disclosing the Functional Potency of Three Oxygenated Monoterpenes in Combating Microbial Pathogenesis: From Targeting Virulence Factors to Chicken Meat Preservation.Foods. 2024 Mar 21;13(6):965. doi: 10.3390/foods13060965. Foods. 2024. PMID: 38540955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toombs-Ruane L.J., Benschop J., French N.P., Biggs P.J., Midwinter A.C., Marshall J.C., Chan M., Drinković D., Fayaz A., Baker M.G., et al. Carriage of Extended-Spectrum-Beta-Lactamase- and AmpC Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Strains from Humans and Pets in the Same Households. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020;86 doi: 10.1128/AEM.01613-20. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ljubojević D., Pelić M., Puvača N., Milanov D. Resistance to Tetracycline in Escherichia coli Isolates from Poultry Meat: Epidemiology, Policy and Perspective. World’s Poult. Sci. J. 2017;73:409–417. doi: 10.1017/S0043933917000216. - DOI
-
- Ljubojević D., Velhner M., Todorović D., Pajić M., Milanov D. Tetracycline Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from Poultry. Arch. Vet. Med. 2016;9:61–81. doi: 10.46784/e-avm.v9i1.97. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

