Construction and Characterization of an Aeromonas hydrophila Multi-Gene Deletion Strain and Evaluation of Its Potential as a Live-Attenuated Vaccine in Grass Carp
- PMID: 34063680
- PMCID: PMC8147641
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines9050451
Construction and Characterization of an Aeromonas hydrophila Multi-Gene Deletion Strain and Evaluation of Its Potential as a Live-Attenuated Vaccine in Grass Carp
Abstract
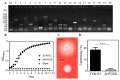
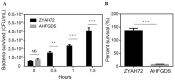
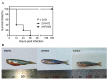
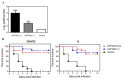
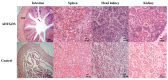
Aeromonas hydrophila is an important pathogen that causes motile Aeromonas septicemia (MAS) in the aquaculture industry. Aerolysin, hemolysin, serine protease and enterotoxins are considered to be the major virulence factors of A. hydrophila. In this study, we constructed a five-gene (aerA, hly, ahp, alt and ast) deletion mutant strain (named Aeromonas hydrophila five-gene deletion strain, AHFGDS) to observe the biological characteristics and detect its potential as a live-attenuated vaccine candidate. AHFGDS displayed highly attenuated and showed increased susceptibility to fish blood and skin mucus killing, while the wild-type strain ZYAH72 was highly virulent. In zebrafish (Danio rerio), AHFGDS showed a 240-fold higher 50% lethal dose (LD50) than that of the wild-type strain. Immunization with AHFGDS by intracelomic injection or immersion routes both provided grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella) significant protection against the challenge of the strain ZYAH72 or J-1 and protected the fish organs from serious injury. Further agglutinating antibody titer test supported that AHFGDS could elicit a host-adaptive immune response. These results suggested the potential of AHFGDS to serve as a live-attenuated vaccine to control A. hydrophila infection in aquaculture.
Keywords: Aeromonas hydrophila; grass carp; immune response; live-attenuated vaccine; virulence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
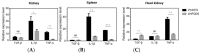
Similar articles
-
Detection of three virulence genes alt, ahp and aerA in Aeromonas hydrophila and their relationship with actual virulence to zebrafish.J Appl Microbiol. 2011 Mar;110(3):823-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.04944.x. Epub 2011 Feb 1. J Appl Microbiol. 2011. PMID: 21219556
-
Construction and characterization of Aeromonas hydrophila crp and fur deletion mutants and evaluation of its potential as live-attenuated vaccines in crucian carp.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024 Mar;146:109380. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2024.109380. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38244821
-
Immune effects of the vaccine of live attenuated Aeromonas hydrophila screened by rifampicin on common carp (Cyprinus carpio L).Vaccine. 2016 Jun 8;34(27):3087-3092. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2016.04.075. Epub 2016 May 4. Vaccine. 2016. PMID: 27155500
-
Vaccination of Tilapia against Motile Aeromonas Septicemia: A Review.J Aquat Anim Health. 2020 Jun;32(2):65-76. doi: 10.1002/aah.10099. Epub 2020 Apr 24. J Aquat Anim Health. 2020. PMID: 32331001 Review.
-
A review on pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila and their mitigation through medicinal herbs in aquaculture.Heliyon. 2023 Feb 28;9(3):e14088. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e14088. eCollection 2023 Mar. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 36938468 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Current status and development prospects of aquatic vaccines.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 10;13:1040336. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1040336. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36439092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Streptomyces enissocaesilis L-82 has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity and promotes growth for Carassius auratus.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 19;108(1):220. doi: 10.1007/s00253-024-13031-7. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38372806 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Bacterial Co-Infections in Farmed Catfish: Components, Diagnostics, and Treatment Directions.Animals (Basel). 2021 Nov 12;11(11):3240. doi: 10.3390/ani11113240. Animals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34827972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tad pili contribute to the virulence and biofilm formation of virulent Aeromonas hydrophila.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Jul 31;14:1425624. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1425624. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39145307 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Hemolymph Microbiota of Chinese Mitten Crab (Eriocheir sinensis) in Response to Aeromonas hydrophila or Staphylococcus aureus Infection.Animals (Basel). 2023 Sep 29;13(19):3058. doi: 10.3390/ani13193058. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835665 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cao Y., Li S., Han S., Wang D., Zhao J., Xu L., Liu H., Lu T. Characterization and application of a novel Aeromonas bacteriophage as treatment for pathogenic Aeromonas hydrophila infection in rainbow trout. Aquaculture. 2020:523. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2020.735193. - DOI
-
- Pridgeon J.W., Yildirim-Aksoy M., Klesius P.H., Srivastava K.K., Reddy P.G. Attenuation of a virulent A eromonas hydrophila with novobiocin and pathogenic characterization of the novobiocin-resistant strain. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012;113:1319–1328. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2012.05430.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rasmussen-Ivey C.R., Hossain M.J., Odom S.E., Terhune J.S., Hemstreet W.G., Shoemaker C.A., Zhang D., Xu D.-H., Griffin M.J., Liu Y.-J., et al. Classification of a Hypervirulent Aeromonas hydrophila Pathotype Responsible for Epidemic Outbreaks in Warm-Water Fishes. Front. Microbiol. 2016;7:1615. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01615. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

