Association of SDF1 and MMP12 with Atherosclerosis and Inflammation: Clinical and Experimental Study
- PMID: 34062730
- PMCID: PMC8147178
- DOI: 10.3390/life11050414
Association of SDF1 and MMP12 with Atherosclerosis and Inflammation: Clinical and Experimental Study
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerosis is the main etiology of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), associated to systemic inflammation. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are related to atherosclerosis progression through the SDF1/CXCR4 axis promoting macrophages recruitment within the vascular wall. The goal was to assess new circulatory inflammatory markers in relation to atherosclerosis.
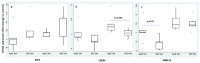
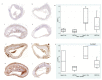
Methods: Measurement of SDF1, MMP12 and CRP in blood samples of 298 prospective patients with cardiovascular risk. To explore atherosclerosis progression, CXCR4/SDF1 axis and MMP12 expression were determined by RT-qPCR and by immunohistochemistry in the aorta of accelerated and delayed atherosclerosis mice models (Apoe-/- and Apoe-/-Mmp10-/-).
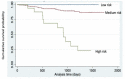
Results: SDF1, MMP12 and CRP were elevated in patients with clinical atherosclerosis, but after controlling by confounding factors, only SDF1 and CRP remained increased. Having high levels of both biomarkers showed 2.8-fold increased risk of presenting clinical atherosclerosis (p = 0.022). Patients with elevated SDF1, MMP12 and CRP showed increased risk of death in follow-up (HR = 3.2, 95%CI: 1.5-7.0, p = 0.004). Gene and protein expression of CXCR4 and MMP12 were increased in aortas from Apoe-/- mice.
Conclusions: The combination of high circulating SDF1, MMP12 and CRP identified patients with particular inflammatory cardiovascular risk and increased mortality. SDF1/CXCR4 axis and MMP12 involvement in atherosclerosis development suggests that they could be possible atherosclerotic targets.
Keywords: MMP-12; SDF1/CXCR4; atherosclerosis; cardiovascular risk; inflammation; multimarker approach.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The sponsors had no role in the design, execution, interpretation, or writing of the study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrative studies implicate matrix metalloproteinase-12 as a culprit gene for large-artery atherosclerotic stroke.J Intern Med. 2017 Nov;282(5):429-444. doi: 10.1111/joim.12655. Epub 2017 Aug 28. J Intern Med. 2017. PMID: 28734077
-
Downregulation of miR-221-3p contributes to IL-1β-induced cartilage degradation by directly targeting the SDF1/CXCR4 signaling pathway.J Mol Med (Berl). 2017 Jun;95(6):615-627. doi: 10.1007/s00109-017-1516-6. Epub 2017 Feb 24. J Mol Med (Berl). 2017. PMID: 28236026
-
Ultrasound Biomicroscopic Imaging for Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist-Inhibiting Atherosclerosis and Markers of Inflammation in Atherosclerotic Development in Apolipoprotein-E Knockout Mice.Tex Heart Inst J. 2015 Aug 1;42(4):319-26. doi: 10.14503/THIJ-14-4318. eCollection 2015 Aug. Tex Heart Inst J. 2015. PMID: 26413013 Free PMC article.
-
High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and atherosclerotic disease: from improved risk prediction to risk-guided therapy.Int J Cardiol. 2013 Oct 15;168(6):5126-34. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2013.07.113. Epub 2013 Aug 24. Int J Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23978367 Review.
-
Lipids, atherosclerosis and CVD risk: is CRP an innocent bystander?Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009 Oct;19(8):521-4. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2009.07.005. Epub 2009 Aug 19. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2009. PMID: 19695857 Review.
Cited by
-
MMP12 is a Potential Predictive and Prognostic Biomarker of Various Cancers Including Lung Adenocarcinoma.Cancer Control. 2024 Jan-Dec;31:10732748241235468. doi: 10.1177/10732748241235468. Cancer Control. 2024. PMID: 38410859 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the Transcription Factor ATF3 as a Direct and Indirect Regulator of the LDLR.Metabolites. 2022 Sep 6;12(9):840. doi: 10.3390/metabo12090840. Metabolites. 2022. PMID: 36144244 Free PMC article.
-
Small interfering RNA-induced silencing lncRNA PVT1 inhibits atherosclerosis via inactivating the MAPK/NF-κB pathway.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Nov 13;13(21):24449-24463. doi: 10.18632/aging.203696. Epub 2021 Nov 13. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34775377 Free PMC article.
-
Novel immune cell infiltration-related biomarkers in atherosclerosis diagnosis.PeerJ. 2023 May 1;11:e15341. doi: 10.7717/peerj.15341. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 37151293 Free PMC article.
-
Choline consumption reduces CVD risk via body composition modification.Sci Rep. 2024 Jul 12;14(1):16152. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66039-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38997295 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Virani S.S., Alonso A., Aparicio H.J., Benjamin E.J., Bittencourt M.S., Callaway C.W., Carson A.P., Chamberlain A.M., Cheng S., Delling F.N., et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2021 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2021;143:e254–e743. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000950. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ridker P.M., MacFadyen J.G., Everett B.M., Libby P., Thuren T., Glynn R.J. Relationship of C-reactive protein reduction to cardiovascular event reduction following treatment with canakinumab: A secondary analysis from the CANTOS randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391:319–328. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32814-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Folsom A.R., Pankow J.S., Tracy R.P., Arnett D.K., Peacock J.M., Hong Y., Djoussé L., Eckfeldt J.H., Investigators of the NHLBI Family Heart Study Association of C-reactive protein with markers of prevalent atherosclerotic disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2001;88:112–117. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9149(01)01603-4. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

