The management of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in intensive care unit (ICU) in low income countries: A review article
- PMID: 34056632
- PMCID: PMC8141348
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nutos.2021.05.001
The management of patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in intensive care unit (ICU) in low income countries: A review article
Abstract
Background: The novel coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome-CoV-2 (SARS-CoV2)- causing coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), outbreak as a world health problem and was declared as a pandemic disease by the world health organization (WHO) in March 2020. Many serious findings have been observed among victims with sever acute respiratory syndrome-CoV-2.
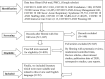
Methods: This review was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-analysis (PRISMA) protocol. Search engines like PubMed and PMC through HINARI, Cochrane database, Google Scholar were used to get information about the current evidences on management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in intensive care unit (ICU).
Discussion: Mortality with COVID 19 is associated with geriatric population, the presence comorbidities like hypertension, diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease, chronic lung disease, and cancer, acute respiratory failure, higher d-dimer and C-reactive protein concentrations, lower lymphocyte counts, and secondary infections.
Conclusion: The international recommendations on nutrition in the ICU should be followed. Some specific issues about the nutrition of the COVID-19 patients in the ICU should be emphasized. Universal infection prevention precautions (hand hygiene and use of personal protection equipment (PPE)) are invaluable during nursing of COVID 19 patients at ICU.
Keywords: Airway; Covid-19; Extubation; ICU; Nutrition.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no competing interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Convalescent plasma or hyperimmune immunoglobulin for people with COVID-19: a rapid review.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 14;5(5):CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jul 10;7:CD013600. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013600.pub2. PMID: 32406927 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Folic acid supplementation and malaria susceptibility and severity among people taking antifolate antimalarial drugs in endemic areas.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 1;2(2022):CD014217. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014217. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36321557 Free PMC article.
-
Intensive care for seriously ill patients affected by novel coronavirus sars - CoV - 2: Experience of the Crema Hospital, Italy.Am J Emerg Med. 2021 Jul;45:156-161. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Aug 16. Am J Emerg Med. 2021. PMID: 33046317 Free PMC article.
-
Human and novel coronavirus infections in children: a review.Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021 Feb;41(1):36-55. doi: 10.1080/20469047.2020.1781356. Epub 2020 Jun 25. Paediatr Int Child Health. 2021. PMID: 32584199 Review.
-
Nutrition of the COVID-19 patient in the intensive care unit (ICU): a practical guidance.Crit Care. 2020 Jul 19;24(1):447. doi: 10.1186/s13054-020-03159-z. Crit Care. 2020. PMID: 32684170 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chakraborty C., Sharma A.R., Sharma G., Bhattacharya M., Lee S.S. SARS-CoV-2 causing pneumonia-associated respiratory disorder (COVID-19): diagnostic and proposed therapeutic options. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(7):4016–4026. - PubMed
-
- Cook T.M., El-Boghdadly K., McGuire B., McNarry A.F., Patel A., Higgs A. Consensus guidelines for managing the airway in patients with COVID-19: guidelines from the difficult airway society, the association of anaesthetists the intensive care society, the faculty of intensive care medicine and the royal college of anaesthetist. Anaesthesia. 2020;75(6):785–799. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
