Bioinformatics identification of hub genes and signaling pathways regulated by intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in acute Kawasaki disease
- PMID: 34055083
- PMCID: PMC8145699
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2021.10216
Bioinformatics identification of hub genes and signaling pathways regulated by intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in acute Kawasaki disease
Abstract
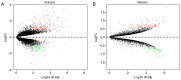
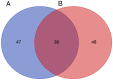
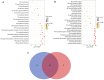
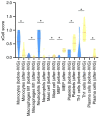
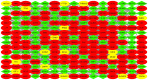
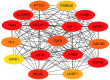
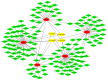
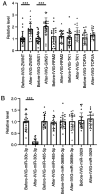
Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute, self-limiting form of vasculitis commonly encountered in infants and young children. Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) is the primary drug used for the treatment of KD, which may significantly reduce the occurrence of coronary artery lesions. However, the specific molecular profile changes of KD caused by IVIG treatment have remained elusive and require further research. The present study was designed to identify key genes, pathways and immune cells affected by IVIG treatment using multiple bioinformatics analysis methods. The results suggested that myeloid cells and neutrophils were affected by IVIG treatment. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis identified that hematopoietic cell lineages and osteoclast differentiation may have an important role in the mechanism of action of IVIG treatment. Immune cell analysis indicated that the levels of monocytes, M1 macrophages, neutrophils and platelets were markedly changed in patients with KD after vs. prior to IVIG treatment. The key upregulated genes, including ZW10 interacting kinetochore protein, GINS complex subunit 1 and microRNA-30b-3p in whole blood cells of patients with KD following treatment with IVIG indicated that these IVIG-targeted molecules may have important roles in KD. In addition, these genes were further examined by literature review and indicated to be involved in cell proliferation, apoptosis and virus-related immune response in patients with KD. Therefore, the present results may provide novel insight into the mechanisms of action of IVIG treatment for KD.
Keywords: Kawasaki disease; bioinformatics analysis; intravenous immunoglobulin; mechanism of action.
Copyright: © Huang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Exploring the relationship between pyroptosis, infiltrating immune cells and Kawasaki disease with resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) via bioinformatic analysis.Immunobiology. 2022 Sep;227(5):152261. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2022.152261. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Immunobiology. 2022. PMID: 36029669
-
Identification of key signaling pathways and hub genes related to immune infiltration in Kawasaki disease with resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 May 30;10:1182512. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1182512. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37325483 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Immune Cell Profile and Changes in Intravenous Immunoglobulin Responsiveness Over the Disease Course in Children With Kawasaki Disease.Front Pediatr. 2022 Feb 4;9:792870. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.792870. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35186822 Free PMC article.
-
Kawasaki disease: a comprehensive review of treatment options.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015 Dec;40(6):620-5. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12334. Epub 2015 Nov 7. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2015. PMID: 26547265 Review.
-
Intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of Kawasaki disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Jan 25;1(1):CD014884. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014884.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36695415 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nomogram to predict risk of resistance to intravenous immunoglobulin in children hospitalized with Kawasaki disease in Eastern China.Ann Med. 2022 Dec;54(1):442-453. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2031273. Ann Med. 2022. PMID: 35099338 Free PMC article.
-
The role of FOXO4/NFAT2 signaling pathway in dysfunction of human coronary endothelial cells and inflammatory infiltration of vasculitis in Kawasaki disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 9;13:1090056. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1090056. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36700213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- de Graeff N, Groot N, Ozen S, Eleftheriou D, Avcin T, Bader-Meunier B, Dolezalova P, Feldman BM, Kone-Paut I, Lahdenne P, et al. European consensus-based recommendations for the diagnosis and treatment of Kawasaki disease - the SHARE initiative. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2019;58:672–682. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/key344. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Beiser AS, Burns JC, Bastian J, Chung KJ, Colan SD, Duffy CE, Fulton DR, Glode MP, et al. A single intravenous infusion of gamma globulin as compared with four infusions in the treatment of acute Kawasaki syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991;324:1633–1639. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199106063242305. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
