Uremic Toxins: An Alarming Danger Concerning the Cardiovascular System
- PMID: 34054588
- PMCID: PMC8160254
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2021.686249
Uremic Toxins: An Alarming Danger Concerning the Cardiovascular System
Abstract
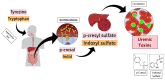
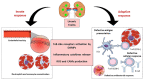
The kidneys and heart share functions with the common goal of maintaining homeostasis. When kidney injury occurs, many compounds, the so-called "uremic retention solutes" or "uremic toxins," accumulate in the circulation targeting other tissues. The accumulation of uremic toxins such as p-cresyl sulfate, indoxyl sulfate and inorganic phosphate leads to a loss of a substantial number of body functions. Although the concept of uremic toxins is dated to the 1960s, the molecular mechanisms capable of leading to renal and cardiovascular injuries are not yet known. Besides, the greatest toxic effects appear to be induced by compounds that are difficult to remove by dialysis. Considering the close relationship between renal and cardiovascular functions, an understanding of the mechanisms involved in the production, clearance and overall impact of uremic toxins is extremely relevant for the understanding of pathologies of the cardiovascular system. Thus, the present study has as main focus to present an extensive review on the impact of uremic toxins in the cardiovascular system, bringing the state of the art on the subject as well as clinical implications related to patient's therapy affected by chronic kidney disease, which represents high mortality of patients with cardiac comorbidities.
Keywords: cardiorenal syndrome; cardiovascular diseases; immune sustem; inflammation; renal diseases; uremic toxins.
Copyright © 2021 Falconi, Junho, Fogaça-Ruiz, Vernier, da Cunha, Stinghen and Carneiro-Ramos.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Cardiotoxicity of Uremic Toxins: A Driver of Cardiorenal Syndrome.Toxins (Basel). 2018 Sep 1;10(9):352. doi: 10.3390/toxins10090352. Toxins (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30200452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Uremic Toxins in the Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Feb 13;13(2):142. doi: 10.3390/toxins13020142. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-bound uremic toxins: new insight from clinical studies.Toxins (Basel). 2011 Jul;3(7):911-9. doi: 10.3390/toxins3070911. Epub 2011 Jul 20. Toxins (Basel). 2011. PMID: 22069747 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p-Cresyl sulfate and indoxyl sulfate in pediatric patients on chronic dialysis.Korean J Pediatr. 2013 Apr;56(4):159-64. doi: 10.3345/kjp.2013.56.4.159. Epub 2013 Apr 22. Korean J Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23646054 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-bound uremic toxin lowering strategies in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Nephrol. 2021 Dec;34(6):1805-1817. doi: 10.1007/s40620-020-00955-2. Epub 2021 Jan 23. J Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33484425
Cited by
-
Gut Microbiota and Metabolic Alterations Associated with Heart Failure and Coronary Artery Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 20;25(20):11295. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011295. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457077 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetic Kidney Disease: Contribution of Phenyl Sulfate Derived from Dietary Tyrosine upon Gut Microbiota Catabolism.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 13;14(9):1153. doi: 10.3390/biom14091153. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Metabolomics Approach to Identify Metabolites Associated With Mortality in Patients Receiving Maintenance Hemodialysis.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Jun 29;9(9):2718-2726. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.06.039. eCollection 2024 Sep. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39291216 Free PMC article.
-
The Worsening of Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Uremic Cardiomyopathy is Further Aggravated by PM2.5 Exposure: Mitochondria Serve as the Central Focus of Pathology.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024 Nov;24(11):1236-1252. doi: 10.1007/s12012-024-09920-y. Epub 2024 Sep 12. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39264521
-
A Systematic Review of Uremic Toxin Concentrations and Cardiovascular Risk Markers in Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Aug 8;16(8):345. doi: 10.3390/toxins16080345. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39195755 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addi T., Poitevin S., McKay N., El Mecherfi K. E., Kheroua O., Jourde-Chiche N., et al. (2019). Mechanisms of tissue factor induction by the uremic toxin indole-3 acetic acid through aryl hydrocarbon receptor/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway in human endothelial cells. Arch. Toxicol. 93 121–136. 10.1007/s00204-018-2328-3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Alexandrou M.-E., Gkaliagkousi E., Loutradis C., Dimitriadis C., Mitsopoulos E., Lazaridis A., et al. (2020). Haemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients have severely impaired post-occlusive skin forearm vasodilatory response assessed with laser speckle contrast imaging. Clin. Kidney J. 2020:sfaa136. 10.1093/ckj/sfaa136 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

