Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for coronavirus disease 2019: which? when? and how much?
- PMID: 34053857
- PMCID: PMC8084615
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2021.04.004
Mesenchymal stromal cell therapy for coronavirus disease 2019: which? when? and how much?
Abstract
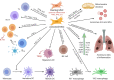
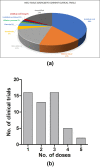
Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) are under active consideration as a treatment strategy for controlling the hyper-inflammation and slow disease progression associated with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). The possible mechanism of protection through their immunoregulatory and paracrine action has been reviewed extensively. However, the importance of process control in achieving consistent cell quality, maximum safety and efficacy-for which the three key questions are which, when and how much-remains unaddressed. Any commonality, if it exists, in ongoing clinical trials has yet to be analyzed and reviewed. In this review, the authors have therefore compiled study design data from ongoing clinical trials to address the key questions of "which" with regard to tissue source, donor profile, isolation technique, culture conditions, long-term culture and cryopreservation of MSCs; "when" with regard to defining the transplantation window by identifying and staging patients based on their pro-inflammatory profile; and "how much" with regard to the number of cells in a single administration, number of doses and route of transplantation. To homogenize MSC therapy for COVID-19 on a global scale and to make it readily available in large numbers, a shared understanding and uniform agreement with respect to these fundamental issues are essential.
Keywords: CD142; MSC dosage; SARS-CoV-2; cytokine storm; hyper-coagulopathy; immunomodulation.
Copyright © 2021 International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cell immunomodulation: In pursuit of controlling COVID-19 related cytokine storm.Stem Cells. 2021 Jun;39(6):707-722. doi: 10.1002/stem.3354. Epub 2021 Mar 7. Stem Cells. 2021. PMID: 33586320 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells: a new front emerges in coronavirus disease 2019 treatment.Cytotherapy. 2022 Aug;24(8):755-766. doi: 10.1016/j.jcyt.2020.07.002. Epub 2020 Jul 15. Cytotherapy. 2022. PMID: 35880307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cell therapies for COVID-19: Current status and mechanism of action.Life Sci. 2020 Dec 1;262:118493. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118493. Epub 2020 Sep 23. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32979360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes to combat Covid-19.Rev Med Virol. 2022 Mar;32(2):e2281. doi: 10.1002/rmv.2281. Epub 2021 Aug 7. Rev Med Virol. 2022. PMID: 34363275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The critical role of mesenchymal stromal/stem cell therapy in COVID-19 patients: An updated review.Cell Biochem Funct. 2021 Dec;39(8):945-954. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3670. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Cell Biochem Funct. 2021. PMID: 34545605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immunomodulatory effect of IFN-γ licensed adipose-mesenchymal stromal cells in an in vitro model of inflammation generated by SARS-CoV-2 antigens.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 16;14(1):24235. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75776-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39415027 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility Study of Cord Tissue Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in COVID-19-Related Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2023 Apr 17;12(4):185-193. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szad009. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 36929827 Free PMC article.
-
Safety of DW-MSC infusion in patients with low clinical risk COVID-19 infection: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Apr 1;13(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02812-4. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35365239 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Updated Living Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Controlled Trials of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to Treat COVID-19: A Framework for Accelerated Synthesis of Trial Evidence for Rapid Approval-FASTER Approval.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022 Jul 20;11(7):675-687. doi: 10.1093/stcltm/szac038. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 35758400 Free PMC article.
-
Allogenic mesenchymal stromal cells and their extracellular vesicles in COVID-19 induced ARDS: a randomized controlled trial.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Jun 26;14(1):169. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03402-8. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37365605 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Symptoms of Coronavirus, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2021 https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html
-
- Kaye R.J. Overview of Stem Cell Therapy for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome with Focus on COVID 19. Pain physician. 2020;23(4S) S421-S432. - PubMed
-
- Manson J.J., Crooks C., Naja M., Ledlie A., Goulden B., Liddle T., Khan E., Mehta P., Martin-Gutierrez L., Waddington K.E., Robinson G.A., Ribeiro Santos L., McLoughlin E., Snell A., Adeney C., Schim van der Loeff I., Baker K.F., Duncan C., Hanrath A.T., Lendrem B.C., …, Tattersall R.S. COVID-19-associated hyperinflammation and escalation of patient care: a retrospective longitudinal cohort study. The Lancet. Rheumatology. 2020;2(10) e594-e602. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

