N6-Methyladenosine on mRNA facilitates a phase-separated nuclear body that suppresses myeloid leukemic differentiation
- PMID: 34048709
- PMCID: PMC8282764
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2021.04.017
N6-Methyladenosine on mRNA facilitates a phase-separated nuclear body that suppresses myeloid leukemic differentiation
Abstract
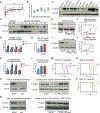
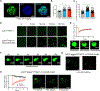
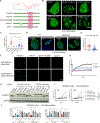
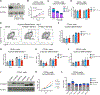
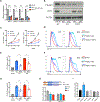
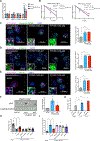
N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) on mRNAs mediates different biological processes and its dysregulation contributes to tumorigenesis. How m6A dictates its diverse molecular and cellular effects in leukemias remains unknown. We found that YTHDC1 is the essential m6A reader in myeloid leukemia from a genome-wide CRISPR screen and that m6A is required for YTHDC1 to undergo liquid-liquid phase separation and form nuclear YTHDC1-m6A condensates (nYACs). The number of nYACs increases in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells compared with normal hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. AML cells require the nYACs to maintain cell survival and the undifferentiated state that is critical for leukemia maintenance. Furthermore, nYACs enable YTHDC1 to protect m6A-mRNAs from the PAXT complex and exosome-associated RNA degradation. Collectively, m6A is required for the formation of a nuclear body mediated by phase separation that maintains mRNA stability and control cancer cell survival and differentiation.
Keywords: RNA methylation; RNA-binding proteins; differentiation; myeloid leukemia; phase separation.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.R.J. is a scientific founder of Gotham Therapeutics and has equity in this company. D. J. P. is a consultant for Ventus Therapeutics. M.G.K. is a consultant for Accent Therapeutics and M.G.K.’s laboratory receives some financial support from 28-7. These disclosures are not directly related to these studies. There is a patent pending.
Figures

Comment in
-
m6A nuclear condensates support AML.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Jul;22(7):442. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00385-3. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34079105 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
High Wilms' tumor 1 associating protein expression predicts poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia and regulates m6A methylation of MYC mRNA.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Jan;147(1):33-47. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03373-w. Epub 2020 Sep 3. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021. PMID: 32880751
-
METTL14 Inhibits Hematopoietic Stem/Progenitor Differentiation and Promotes Leukemogenesis via mRNA m6A Modification.Cell Stem Cell. 2018 Feb 1;22(2):191-205.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2017.11.016. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Cell Stem Cell. 2018. PMID: 29290617 Free PMC article.
-
A critical role of nuclear m6A reader YTHDC1 in leukemogenesis by regulating MCM complex-mediated DNA replication.Blood. 2021 Dec 30;138(26):2838-2852. doi: 10.1182/blood.2021011707. Blood. 2021. PMID: 34255814 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted effects of YTHDC1-mediated nuclear m6A recognition.Trends Genet. 2022 Apr;38(4):325-332. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.11.005. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Trends Genet. 2022. PMID: 34920906 Review.
-
Functions of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA modifications in acute myeloid leukemia.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Oct 1;116(4):662-671. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae106. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38721720 Review.
Cited by
-
RNA modification in normal hematopoiesis and hematologic malignancies.MedComm (2020). 2024 Oct 23;5(11):e787. doi: 10.1002/mco2.787. eCollection 2024 Nov. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39445003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YTHDC1-mediated microRNA maturation is essential for hematopoietic stem cells maintenance.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Oct 16;10(1):439. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02203-z. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39414764 Free PMC article.
-
Reading the m6A-encoded epitranscriptomic information in development and diseases.Cell Biosci. 2024 Sep 28;14(1):124. doi: 10.1186/s13578-024-01293-7. Cell Biosci. 2024. PMID: 39342406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-canonical translation in cancer: significance and therapeutic potential of non-canonical ORFs, m6A-modification, and circular RNAs.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Sep 27;10(1):412. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02185-y. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39333489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The m6A regulators in prostate cancer: molecular basis and clinical perspective.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 29;15:1448872. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1448872. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39268470 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

