Architecture of the Sema3A/PlexinA4/Neuropilin tripartite complex
- PMID: 34039996
- PMCID: PMC8155012
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23541-x
Architecture of the Sema3A/PlexinA4/Neuropilin tripartite complex
Abstract
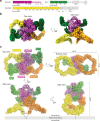
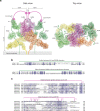
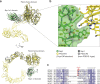
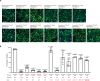
Secreted class 3 semaphorins (Sema3s) form tripartite complexes with the plexin receptor and neuropilin coreceptor, which are both transmembrane proteins that together mediate semaphorin signal for neuronal axon guidance and other processes. Despite extensive investigations, the overall architecture of and the molecular interactions in the Sema3/plexin/neuropilin complex are incompletely understood. Here we present the cryo-EM structure of a near intact extracellular region complex of Sema3A, PlexinA4 and Neuropilin 1 (Nrp1) at 3.7 Å resolution. The structure shows a large symmetric 2:2:2 assembly in which each subunit makes multiple interactions with others. The two PlexinA4 molecules in the complex do not interact directly, but their membrane proximal regions are close to each other and poised to promote the formation of the intracellular active dimer for signaling. The structure reveals a previously unknown interface between the a2b1b2 module in Nrp1 and the Sema domain of Sema3A. This interaction places the a2b1b2 module at the top of the complex, far away from the plasma membrane where the transmembrane regions of Nrp1 and PlexinA4 embed. As a result, the region following the a2b1b2 module in Nrp1 must span a large distance to allow the connection to the transmembrane region, suggesting an essential role for the long non-conserved linkers and the MAM domain in neuropilin in the semaphorin/plexin/neuropilin complex.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Plexin/neuropilin complexes mediate repulsion by the axonal guidance signal semaphorin 3A.Mech Dev. 2000 May;93(1-2):95-104. doi: 10.1016/s0925-4773(00)00269-0. Mech Dev. 2000. PMID: 10781943
-
Semaphorin 3A activates the guanosine triphosphatase Rab5 to promote growth cone collapse and organize callosal axon projections.Sci Signal. 2014 Aug 26;7(340):ra81. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2005334. Sci Signal. 2014. PMID: 25161316 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions between semaphorins and plexin-neuropilin receptor complexes in the membranes of live cells.J Biol Chem. 2021 Aug;297(2):100965. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100965. Epub 2021 Jul 13. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34270956 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular basis of semaphorin-mediated axon guidance.J Neurobiol. 2000 Aug;44(2):219-29. doi: 10.1002/1097-4695(200008)44:2<219::aid-neu11>3.0.co;2-w. J Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 10934324 Review.
-
Structural and functional relation of neuropilins.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:55-69. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0119-0_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002. PMID: 12613543 Review.
Cited by
-
Modelling and Refining Neuronal Circuits with Guidance Cues: Involvement of Semaphorins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 6;22(11):6111. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116111. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34204060 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropilin 1 (NRP1) Positively Regulates Adipogenic Differentiation in C3H10T1/2 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 17;24(8):7394. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087394. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108554 Free PMC article.
-
A single-cell atlas of West African lungfish respiratory system reveals evolutionary adaptations to terrestrialization.Nat Commun. 2023 Sep 13;14(1):5630. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41309-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37699889 Free PMC article.
-
New Crystal Form of Human Neuropilin-1 b1 Fragment with Six Electrostatic Mutations Complexed with KDKPPR Peptide Ligand.Molecules. 2023 Jul 24;28(14):5603. doi: 10.3390/molecules28145603. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37513474 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Semaphorin 3A in Kidney Development and Diseases.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Sep 25;13(19):3038. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13193038. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835781 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

