Immunity-longevity tradeoff neurally controlled by GABAergic transcription factor PITX1/UNC-30
- PMID: 34038721
- PMCID: PMC8227953
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109187
Immunity-longevity tradeoff neurally controlled by GABAergic transcription factor PITX1/UNC-30
Abstract
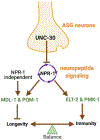
A body of evidence indicates that metazoan immune and aging pathways are largely interconnected, but the mechanisms involved in their homeostatic control remain unclear. In this study, we find that the PITX (paired-like homeodomain) transcription factor UNC-30 controls the tradeoff between immunity and longevity from the nervous system in Caenorhabditis elegans. PITX/UNC-30 functional loss enhances immunity in a GATA/ELT-2- and p38 MAPK/PMK-1-dependent manner and reduced longevity by activating MXD/MDL-1 and the C2H2-type zinc finger transcription factor PQM-1. The immune inhibitory and longevity stimulatory functions of PITX/UNC-30 require the sensory neuron ASG and a signaling pathway controlled by NPR-1, which is a G protein-coupled receptor related to mammalian neuropeptide Y receptors. Our findings uncover a suppressive role of GABAergic signaling in the neural control of a biological tradeoff where energy is allocated toward immunity at the expense of longevity.
Keywords: C. elegans; GABAergic; P. aeruginosa; immunity; infection; innate; longevity; neuropeptides; neurotransmitters; tradeoff.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
p38 MAPK regulates expression of immune response genes and contributes to longevity in C. elegans.PLoS Genet. 2006 Nov 10;2(11):e183. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.0020183. Epub 2006 Sep 11. PLoS Genet. 2006. PMID: 17096597 Free PMC article.
-
GABAergic synapses suppress intestinal innate immunity via insulin signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 May 18;118(20):e2021063118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2021063118. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021. PMID: 33972423 Free PMC article.
-
Deficiency of Innate Immunity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa Enhances Behavioral Avoidance via the HECW-1/NPR-1 Module in Caenorhabditis elegans.Infect Immun. 2021 Sep 16;89(10):e0006721. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00067-21. Epub 2021 Jul 26. Infect Immun. 2021. PMID: 34310887 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of aging and innate immunity in C. elegans.Aging Cell. 2004 Aug;3(4):185-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9728.2004.00108.x. Aging Cell. 2004. PMID: 15268752 Review.
-
Insights from the worm: the C. elegans model for innate immunity.Semin Immunol. 2014 Aug;26(4):303-9. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2014.04.005. Epub 2014 May 21. Semin Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24856329 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ELO-6 expression predicts longevity in isogenic populations of Caenorhabditis elegans.Nat Commun. 2024 Nov 2;15(1):9470. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53887-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39488532 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating p38 MAPK signaling by proteostasis mechanisms supports tissue integrity during growth and aging.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 28;14(1):4543. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-40317-7. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37507441 Free PMC article.
-
Amphid sensory neurons of Caenorhabditis elegans orchestrate its survival from infection with broad classes of pathogens.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 May 31;6(8):e202301949. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202301949. Print 2023 Aug. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37258276 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal NPR-15 modulates molecular and behavioral immune responses via the amphid sensory neuron-intestinal axis in C. elegans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 30:2023.07.27.550570. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.27.550570. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Elife. 2024 Mar 06;12:RP90051. doi: 10.7554/eLife.90051 PMID: 37546751 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Curcumin supplementation increases longevity and antioxidant capacity in Caenorhabditis elegans.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 6;14:1195490. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1195490. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37346299 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aballay A, Drenkard E, Hilbun LR, and Ausubel FM (2003). Caenorhabditis elegans innate immune response triggered by Salmonella enterica requires intact LPS and is mediated by a MAPK signaling pathway. Curr. Biol 13, 47–52. - PubMed
-
- Alcedo J, and Kenyon C (2004). Regulation of C. elegans longevity by specific gustatory and olfactory neurons. Neuron 41, 45–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

