A community effort to identify and correct mislabeled samples in proteogenomic studies
- PMID: 34036290
- PMCID: PMC8134945
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patter.2021.100245
A community effort to identify and correct mislabeled samples in proteogenomic studies
Abstract
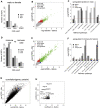
Sample mislabeling or misannotation has been a long-standing problem in scientific research, particularly prevalent in large-scale, multi-omic studies due to the complexity of multi-omic workflows. There exists an urgent need for implementing quality controls to automatically screen for and correct sample mislabels or misannotations in multi-omic studies. Here, we describe a crowdsourced precisionFDA NCI-CPTAC Multi-omics Enabled Sample Mislabeling Correction Challenge, which provides a framework for systematic benchmarking and evaluation of mislabel identification and correction methods for integrative proteogenomic studies. The challenge received a large number of submissions from domestic and international data scientists, with highly variable performance observed across the submitted methods. Post-challenge collaboration between the top-performing teams and the challenge organizers has created an open-source software, COSMO, with demonstrated high accuracy and robustness in mislabeling identification and correction in simulated and real multi-omic datasets.
Keywords: DSML 3: Development/Pre-production: Data science output has been rolled out/validated across multiple domains/problems.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
S.Y. and J.Z. are employees of Sema4, a for-profit organization that promotes a healthcare through information-driven insights. R.P., H.F., and H.C. are employees of Sentieon Inc. A.C. is an employee of Bionamic AB. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
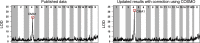
Similar articles
-
Right data for right patient-a precisionFDA NCI-CPTAC Multi-omics Mislabeling Challenge.Nat Med. 2018 Sep;24(9):1301-1302. doi: 10.1038/s41591-018-0180-x. Nat Med. 2018. PMID: 30194412 Free PMC article.
-
Inaccurate Labels in Weakly-Supervised Deep Learning: Automatic Identification and Correction and Their Impact on Classification Performance.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2020 Sep;24(9):2701-2710. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.2974425. Epub 2020 Feb 17. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2020. PMID: 32078570 Free PMC article.
-
DECONbench: a benchmarking platform dedicated to deconvolution methods for tumor heterogeneity quantification.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 Oct 2;22(1):473. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04381-4. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34600479 Free PMC article.
-
Single-platform 'multi-omic' profiling: unified mass spectrometry and computational workflows for integrative proteomics-metabolomics analysis.Mol Omics. 2018 Oct 8;14(5):307-319. doi: 10.1039/c8mo00136g. Mol Omics. 2018. PMID: 30211418 Review.
-
Multi-omic and multi-view clustering algorithms: review and cancer benchmark.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Nov 16;46(20):10546-10562. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky889. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 30295871 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Quartet Data Portal: integration of community-wide resources for multiomics quality control.Genome Biol. 2023 Oct 26;24(1):245. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-03091-9. Genome Biol. 2023. PMID: 37884999 Free PMC article.
-
SMAP is a pipeline for sample matching in proteogenomics.Nat Commun. 2022 Feb 8;13(1):744. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28411-8. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35136070 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue heterogeneity is prevalent in gene expression studies.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2021 Sep 3;3(3):lqab077. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqab077. eCollection 2021 Sep. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 34514392 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

