Modified secreted alkaline phosphatase as an improved reporter protein for N-glycosylation analysis
- PMID: 34032812
- PMCID: PMC8148361
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0251805
Modified secreted alkaline phosphatase as an improved reporter protein for N-glycosylation analysis
Abstract
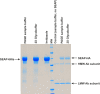
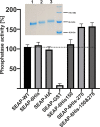
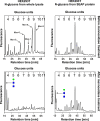
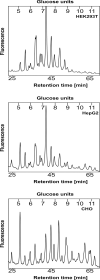
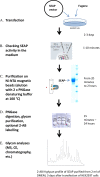
N-glycosylation is a common posttranslational modification of proteins in eukaryotic cells. The modification is often analyzed in cells which are able to produce extracellular, glycosylated proteins. Here we report an improved method of the use of genetically modified, secreted alkaline phosphatase (SEAP) as a reporter glycoprotein which may be used for glycoanalysis. Additional N-glycosylation sites introduced by site-directed mutagenesis significantly increased secretion of the protein. An improved purification protocol of recombinant SEAP from serum or serum-free media is also proposed. The method enables fast and efficient separation of reporter glycoprotein from a relatively small amount of medium (0.5-10 ml) with a high recovery level. As a result, purified SEAP was ready for enzymatic de-glycosylation without buffer exchange, sample volume reductions or other procedures, which are usually time-consuming and may cause partial loss of the reporter glycoprotein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of production method and gene amplification on the glycosylation pattern of a secreted reporter protein in CHO cells.Biotechnol Prog. 2005 Jan-Feb;21(1):40-9. doi: 10.1021/bp049761m. Biotechnol Prog. 2005. PMID: 15903239
-
Effect of silkworm hemolymph on N-linked glycosylation in two Trichoplusia ni insect cell lines.Biotechnol Bioeng. 2003 Sep 20;83(6):695-705. doi: 10.1002/bit.10696. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2003. PMID: 12889034
-
Recombinant Expression and Purification of Mouse Nectin-like 4 Glycoprotein in 293ET Cell Line.Chin Med Sci J. 2018 Mar 30;33(1):1-8. doi: 10.24920/11805. Chin Med Sci J. 2018. PMID: 29620509
-
Recombinant glycoprotein production in human cell lines.Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1258:223-40. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-2205-5_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25447867 Review.
-
Glycoengineering of CHO Cells to Improve Product Quality.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1603:25-44. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6972-2_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28493121 Review.
Cited by
-
S9.6 Antibody-Enzyme Conjugates for the Detection of DNA-RNA Hybrids.Bioconjug Chem. 2023 May 17;34(5):834-844. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.2c00609. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Bioconjug Chem. 2023. PMID: 37194248 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding glycosylation potential from protein structure across human glycoproteins with a multi-view recurrent neural network.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 23:2024.05.15.594334. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.15.594334. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38798633 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Schjoldager K. T., Narimatsu Y., Joshi H. J., Clausen H.. Global view of human protein glycoslation pathways and functions. Nature Review Mol Cell Biol, 21 (2020), 729–749. - PubMed
-
- Etzler M.E. (Ed.), Essential of Glycobiology, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 2009. - PubMed
-
- An H. J., Gip P., Kim J., Wu S., Park K.W., McVaugh C. T., et al.., Extensive determination of glycan heterogeneity reveals an unusual abundance of high mannose glycans in enriched plasma membranes of human embryonic stem cells, Mol. Cell. Proteomics 11 (2012), M111.010660. 10.1074/mcp.M111.010660 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Homouda H., Kaup M., Ullach M., Berger M., Sandig V., Tauber R., et al.., Rapid analysis of cell surface N-glycosylation from living cells using mass spectrometry, J. Proteom. Res. 13 (2014), 6144–6151. - PubMed
-
- Hamouda H., Ullah M., Berger M., Sittinger M., Tauber R., Ringe J., et al., N-Glycosylation profile of undifferentiated and adipogenically differentiated human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: towards a next generation of stem cell markers, Stem. Cells. Dev. 22 (2013), 3100−13. 10.1089/scd.2013.0108 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

