Electrostatic Interaction Between NS1 and Negatively Charged Lipids Contributes to Flavivirus Replication Organelles Formation
- PMID: 34025602
- PMCID: PMC8138564
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.641059
Electrostatic Interaction Between NS1 and Negatively Charged Lipids Contributes to Flavivirus Replication Organelles Formation
Abstract
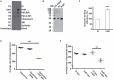
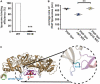
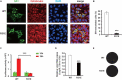
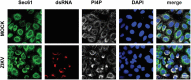
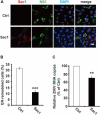
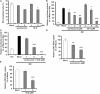
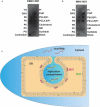
Flavivirus replication occurs in membranous replication compartments, also known as replication organelles (ROs) derived from the host ER membrane. Our previous study showed that the non-structural (NS) protein 1 (NS1) is the essential factor for RO creation by hydrophobic insertion into the ER membrane. Here, we found that the association of NS1 with the membrane can be facilitated by the electrostatic interaction between NS1 and negatively charged lipids. NS1 binds to a series of negatively charged lipids, including PI4P, and a positively charged residue, R31, located on the membrane-binding face of NS1, plays important roles in this interaction. The NS1 R31E mutation significantly impairs NS1 association with negatively charged membrane and its ER remodeling ability in the cells. To interfere with the electrostatic interaction between NS1 and negatively charged lipids, intracellular phosphatidylinositol phosphates (PIPs) level was downregulated by the overexpression of Sac1 or treatment with PI3K and PI4K inhibitors to attenuate flavivirus replication. Our findings emphasize the importance of electrostatic interaction between NS1 and negatively charged lipids in flavivirus RO formation.
Keywords: ER remodeling; PIP; flavivirus; non-structural protein 1; replication organelles.
Copyright © 2021 Ci, Yang, Xu, Qin and Shi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The glycosylation deficiency of flavivirus NS1 attenuates virus replication through interfering with the formation of viral replication compartments.J Biomed Sci. 2024 Jun 7;31(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s12929-024-01048-z. J Biomed Sci. 2024. PMID: 38849802 Free PMC article.
-
Zika NS1-induced ER remodeling is essential for viral replication.J Cell Biol. 2020 Feb 3;219(2):e201903062. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201903062. J Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31868887 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in Encephalomyocarditis Virus 3A Protein Uncouple the Dependency of Genome Replication on Host Factors Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase IIIα and Oxysterol-Binding Protein.mSphere. 2016 May 11;1(3):e00068-16. doi: 10.1128/mSphere.00068-16. eCollection 2016 May-Jun. mSphere. 2016. PMID: 27303747 Free PMC article.
-
The flavivirus NS1 protein: molecular and structural biology, immunology, role in pathogenesis and application as a diagnostic biomarker.Antiviral Res. 2013 May;98(2):192-208. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.03.008. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Antiviral Res. 2013. PMID: 23523765 Review.
-
Secretion of flaviviral non-structural protein NS1: from diagnosis to pathogenesis.Novartis Found Symp. 2006;277:233-47; discussion 247-53. doi: 10.1002/0470058005.ch17. Novartis Found Symp. 2006. PMID: 17319166 Review.
Cited by
-
Bithiazole Inhibitors of Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase (PI4KIIIβ) as Broad-Spectrum Antivirals Blocking the Replication of SARS-CoV-2, Zika Virus, and Human Rhinoviruses.ChemMedChem. 2021 Dec 6;16(23):3548-3552. doi: 10.1002/cmdc.202100483. Epub 2021 Sep 7. ChemMedChem. 2021. PMID: 34382337 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Are Conveyors of the NS1 Toxin during Dengue Virus and Zika Virus Infection.Viruses. 2023 Jan 27;15(2):364. doi: 10.3390/v15020364. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36851578 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in the Membrane-Binding Properties of Flaviviral Nonstructural 1 (NS1) Protein: Comparative Simulations of Zika and Dengue Virus NS1 Proteins in Explicit Bilayers.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2024 Mar 15;4(3):137-153. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.3c00073. eCollection 2024 Jun 19. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2024. PMID: 38911907 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

