Screening for extremely rare pathogenic variants of monogenic diabetes using targeted panel sequencing
- PMID: 34019234
- PMCID: PMC8325655
- DOI: 10.1007/s12020-021-02753-7
Screening for extremely rare pathogenic variants of monogenic diabetes using targeted panel sequencing
Abstract
Aims: Maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) is one of the rare monogenic forms of diabetes. To date, about 12 genes in the scientific literature are closely related to the occurrence of the disease phenotype. However, there is still a high prevalence of undiagnosed cases of so-called MODY-X whose genetic background is still unknown.
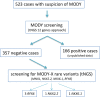
Methods: We performed tNGS for 523 patients with suspected MODY. Next 357 selected patients, in whom no damaging variants were found in 12 major genes causing MODY, were screened for the presence of pathogenic variants in four candidate genes (MNX1, RFX6, NKX2.2, and NKX6.1). All data were generated in one tNGS sequencing reaction and confirmed by Sanger sequencing.
Results: In total, we selected five potentially damaging variants, in eight patients, in RFX6, NKX2.2, and NKX6.1 genes. Four of them have never been described in literature before. The frequency of occurrence of two of them in the RFX6 gene significantly differed in relation to the healthy population. The analysis of segregation in the family did not reveal that they were the only cause of the disease phenotype.
Conclusions: The very-rare variants indicated in this study show that this type of research on large population groups may help in the future for better understanding and more accurate diagnostics of extremely rare forms of MODY.
Keywords: MODY; Monogenic diabetes; Next-generation sequencing; Rare variant.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification of rare variants in candidate genes associated with monogenic diabetes in polish mody-x patients.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Oct 13;23(1):545-554. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01312-3. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 38932873 Free PMC article.
-
MODY Only Monogenic? A Narrative Review of the Novel Rare and Low-Penetrant Variants.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8790. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168790. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted sequencing identifies novel variants in common and rare MODY genes.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019 Dec;7(12):e962. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.962. Epub 2019 Oct 8. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2019. PMID: 31595705 Free PMC article.
-
The Application of Next Generation Sequencing Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young Gene Panel in Turkish Patients from Trakya Region.J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2021 Aug 23;13(3):320-331. doi: 10.4274/jcrpe.galenos.2021.2020.0285. Epub 2021 Feb 10. J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 33565752 Free PMC article.
-
Undiagnosed MODY: Time for Action.Curr Diab Rep. 2015 Dec;15(12):110. doi: 10.1007/s11892-015-0681-7. Curr Diab Rep. 2015. PMID: 26458381 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Search for a time- and cost-saving genetic testing strategy for maturity-onset diabetes of the young.Acta Diabetol. 2022 Sep;59(9):1169-1178. doi: 10.1007/s00592-022-01915-x. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Acta Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35737141 Free PMC article.
-
Initial clinical manifestations in a young male with RFX6-variant-associated diabetes.Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2024 Oct;33(4):224-228. doi: 10.1297/cpe.2024-0016. Epub 2024 Jul 20. Clin Pediatr Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 39359667 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of rare variants in candidate genes associated with monogenic diabetes in polish mody-x patients.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023 Oct 13;23(1):545-554. doi: 10.1007/s40200-023-01312-3. eCollection 2024 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2023. PMID: 38932873 Free PMC article.
-
MODY Only Monogenic? A Narrative Review of the Novel Rare and Low-Penetrant Variants.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8790. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168790. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201476 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Frayling TM, Evans JC, Bulman MP, Pearson E, Allen L, Owen K, Bingham C, Hannemann M, Shepherd M, Ellard S, Hattersley AT. eta-cell genes and diabetes: molecular and clinical characterization of mutations in transcription factors. Diabetes. 2001;50(Suppl 1):S94–100. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.2007.s94. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonnefond A, Philippe J, Durand E, Dechaume A, Huyvaert M, Montagne L, Marre M, Balkau B, Fajardy I, Vambergue A, Vatin V, Delplanque J, Le Guilcher D, De Graeve F, Lecoeur C, Sand O, Vaxillaire M, Froguel P. Whole-exome sequencing and high throughput genotyping identified KCNJ11 as the thirteenth MODY gene. PloS ONE. 2012;7(6):e37423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037423. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Santana LS, Caetano LA, Costa-Riquetto AD, Quedas EPS, Nery M, Collett-Solberg P, Boguszewski MCS, Vendramini MF, Crisostomo LG, Floh FO, Zarabia ZI, Kohara SK, Guastapaglia L, Passone CGB, Sewaybricker LE, Jorge AAL, Teles MG. Clinical application of ACMG-AMP guidelines in HNF1A and GCK variants in a cohort of MODY families. Clin. Genet. 2017;92(4):388–396. doi: 10.1111/cge.12988. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical