Examination of BDNF Treatment on BACE1 Activity and Acute Exercise on Brain BDNF Signaling
- PMID: 34017238
- PMCID: PMC8129185
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2021.665867
Examination of BDNF Treatment on BACE1 Activity and Acute Exercise on Brain BDNF Signaling
Abstract
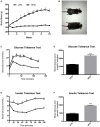
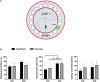
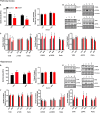
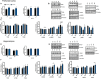
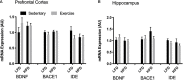
Perturbations in metabolism results in the accumulation of beta-amyloid peptides, which is a pathological feature of Alzheimer's disease. Beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE1) is the rate limiting enzyme responsible for beta-amyloid production. Obesogenic diets increase BACE1 while exercise reduces BACE1 activity, although the mechanisms are unknown. Brain-derived neurotropic factor (BDNF) is an exercise inducible neurotrophic factor, however, it is unknown if BDNF is related to the effects of exercise on BACE1. The purpose of this study was to determine the direct effect of BDNF on BACE1 activity and to examine neuronal pathways induced by exercise. C57BL/6J male mice were assigned to either a low (n = 36) or high fat diet (n = 36) for 10 weeks. To determine the direct effect of BDNF on BACE1, a subset of mice (low fat diet = 12 and high fat diet n = 12) were used for an explant experiment where the brain tissue was directly treated with BDNF (100 ng/ml) for 30 min. To examine neuronal pathways activated with exercise, mice remained sedentary (n = 12) or underwent an acute bout of treadmill running at 15 m/min with a 5% incline for 120 min (n = 12). The prefrontal cortex and hippocampus were collected 2-h post-exercise. Direct treatment with BDNF resulted in reductions in BACE1 activity in the prefrontal cortex (p < 0.05), but not the hippocampus. The high fat diet reduced BDNF content in the hippocampus; however, the acute bout of exercise increased BDNF in the prefrontal cortex (p < 0.05). These novel findings demonstrate the region specific differences in exercise induced BDNF in lean and obese mice and show that BDNF can reduce BACE1 activity, independent of other exercise-induced alterations. This work demonstrates a previously unknown link between BDNF and BACE1 regulation.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; BDNF; beta-secretase; exercise; obesity.
Copyright © 2021 Baranowski, Hayward, Marko and MacPherson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acute exercise and brain BACE1 protein content: a time course study.Physiol Rep. 2019 Apr;7(8):e14084. doi: 10.14814/phy2.14084. Physiol Rep. 2019. PMID: 31033251 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise training and BDNF injections alter amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing enzymes and improve cognition.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2023 Jul 1;135(1):121-135. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00114.2023. Epub 2023 Jun 1. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2023. PMID: 37262102
-
Acute exercise induced BDNF-TrkB signalling is intact in the prefrontal cortex of obese, glucose-intolerant male mice.Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018 Oct;43(10):1083-1089. doi: 10.1139/apnm-2018-0108. Epub 2018 May 4. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2018. PMID: 29726700
-
Filling the void: a role for exercise-induced BDNF and brain amyloid precursor protein processing.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;313(5):R585-R593. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00255.2017. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28814391 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The beta-secretase, BACE: a prime drug target for Alzheimer's disease.J Mol Neurosci. 2001 Oct;17(2):157-70. doi: 10.1385/JMN:17:2:157. J Mol Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11816789 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of Central and Peripheral Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a Biomarker of Anorexia Nervosa Reconceptualized as a Metabo-Psychiatric Disorder.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 8;16(16):2617. doi: 10.3390/nu16162617. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39203753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Examination of Akt and GSK3β in BDNF-mediated reductions in BACE1 activity in neuronal cells.Physiol Rep. 2024 Aug;12(16):e70001. doi: 10.14814/phy2.70001. Physiol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39161054 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise mimetics: a novel strategy to combat neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Feb 2;21(1):40. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03031-9. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38308368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone acetylation in an Alzheimer's disease cell model promotes homeostatic amyloid-reducing pathways.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024 Jan 2;12(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01696-6. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2024. PMID: 38167174 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of metabolic stress and metformin on synaptic protein profile in SH-SY5Y-derived neurons.Physiol Rep. 2023 Nov;11(22):10.14814/phy2.15852. doi: 10.14814/phy2.15852. Physiol Rep. 2023. PMID: 38010200 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

