Single-molecule imaging of epigenetic complexes in living cells: insights from studies on Polycomb group proteins
- PMID: 34009336
- PMCID: PMC8266577
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkab304
Single-molecule imaging of epigenetic complexes in living cells: insights from studies on Polycomb group proteins
Abstract
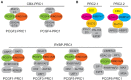
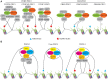
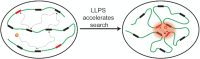
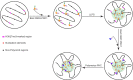
Chromatin-associated factors must locate, bind to, and assemble on specific chromatin regions to execute chromatin-templated functions. These dynamic processes are essential for understanding how chromatin achieves regulation, but direct quantification in living mammalian cells remains challenging. Over the last few years, live-cell single-molecule tracking (SMT) has emerged as a new way to observe trajectories of individual chromatin-associated factors in living mammalian cells, providing new perspectives on chromatin-templated activities. Here, we discuss the relative merits of live-cell SMT techniques currently in use. We provide new insights into how Polycomb group (PcG) proteins, master regulators of development and cell differentiation, decipher genetic and epigenetic information to achieve binding stability and highlight that Polycomb condensates facilitate target-search efficiency. We provide perspectives on liquid-liquid phase separation in organizing Polycomb targets. We suggest that epigenetic complexes integrate genetic and epigenetic information for target binding and localization and achieve target-search efficiency through nuclear organization.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Nuclear condensates of the Polycomb protein chromobox 2 (CBX2) assemble through phase separation.J Biol Chem. 2019 Feb 1;294(5):1451-1463. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.006620. Epub 2018 Dec 4. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30514760 Free PMC article.
-
Phase-Separated Transcriptional Condensates Accelerate Target-Search Process Revealed by Live-Cell Single-Molecule Imaging.Cell Rep. 2020 Oct 13;33(2):108248. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108248. Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 33053359 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular architecture of polycomb repressive complexes.Biochem Soc Trans. 2017 Feb 8;45(1):193-205. doi: 10.1042/BST20160173. Biochem Soc Trans. 2017. PMID: 28202673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Live-cell single-molecule dynamics of PcG proteins imposed by the DIPG H3.3K27M mutation.Nat Commun. 2018 May 25;9(1):2080. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04455-7. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29802243 Free PMC article.
-
Polycomb group proteins and their roles in regulating stem cell development.Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2012 Jun;34(3):281-5. doi: 10.3881/j.issn.1000-503X.2012.03.019. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22776663 Review.
Cited by
-
PR-DUB safeguards Polycomb repression through H2AK119ub1 restriction.Cell Prolif. 2023 Oct;56(10):e13457. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13457. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36959757 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying the global binding and target-search dynamics of epigenetic regulatory factors using live-cell single-molecule tracking.STAR Protoc. 2021 Nov 16;2(4):100959. doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2021.100959. eCollection 2021 Dec 17. STAR Protoc. 2021. PMID: 34825219 Free PMC article.
-
Sparse CBX2 nucleates many Polycomb proteins to promote facultative heterochromatinization of Polycomb target genes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Feb 5:2024.02.05.578969. doi: 10.1101/2024.02.05.578969. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38370615 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Impact of Saccharomyces cerevisiae on the Field of Single-Molecule Biophysics.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 14;23(24):15895. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415895. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555532 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Single-molecule studies of DNA-protein interactions collection 2021.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jun 21;49(11):6005-6006. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab497. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 34153108 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Li B., Carey M., Workman J.L.. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell. 2007; 128:707–719. - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007; 128:693–705. - PubMed
-
- Halford S.E. An end to 40 years of mistakes in DNA-protein association kinetics?. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2009; 37:343–348. - PubMed
-
- Normanno D., Dahan M., Darzacq X.. Intra-nuclear mobility and target search mechanisms of transcription factors: a single-molecule perspective on gene expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2012; 1819:482–493. - PubMed
-
- Suter D.M. Transcription factors and DNA play hide and seek. Trends Cell Biol. 2020; 30:491–500. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

