The role of tumor necrosis factor-α and interferon-γ in the hyperglycemia-induced ubiquitination and loss of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 in rat retinal endothelial cells
- PMID: 34008903
- PMCID: PMC10078990
- DOI: 10.1111/micc.12717
The role of tumor necrosis factor-α and interferon-γ in the hyperglycemia-induced ubiquitination and loss of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 in rat retinal endothelial cells
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the role of the hyperglycemia-induced increase in tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ) in the ubiquitination and degradation of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (PECAM-1) in the diabetic retina.
Methods: Type I diabetes was induced in rats by the injection of streptozotocin, with age-matched non-diabetic rats as controls. Primary rat retinal microvascular endothelial cells were grown in normal or high glucose media for 6 days or in normal glucose media for 24 h with addition of TNF-α and/or IFN-γ. PECAM-1, TNF-α, IFN-γ, and ubiquitin levels were assessed using Western blotting, immunofluorescence, and immunoprecipitation assays. Additionally, proteasome activity was assessed both in vivo and in vitro.
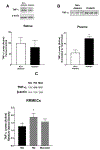
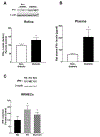
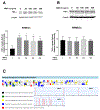
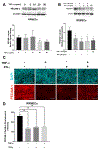
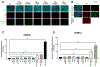
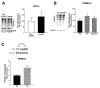
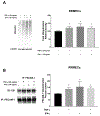
Results: Under hyperglycemic conditions, total ubiquitination levels in the retina and RRMECs, and PECAM-1 ubiquitination levels in RRMECs, were significantly increased. Additionally, TNF-α and IFN-γ levels were significantly increased under hyperglycemic conditions. PECAM-1 levels in RRMECs treated with TNF-α and/or IFN-γ were significantly decreased. Moreover, there was a significant decrease in proteasome activity in the diabetic retina, hyperglycemic RRMECs, and RRMECs treated with TNF-α or IFN-γ.
Conclusion: Tumor necrosis factor-α and IFN-γ may contribute to the hyperglycemia-induced loss of PECAM-1 in retinal endothelial cells, possibly by upregulating PECAM-1 ubiquitination.
Keywords: IFN-γ; PECAM-1; TNF-α; diabetic retinopathy; ubiquitination.
© 2021 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
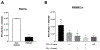
Similar articles
-
Loss of Platelet Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (PECAM-1) in the Diabetic Retina: Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019 Feb 1;60(2):748-760. doi: 10.1167/iovs.18-25068. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019. PMID: 30793207 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia-induced ubiquitination and degradation of β-catenin with the loss of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 in retinal endothelial cells.Microcirculation. 2020 Feb;27(2):e12596. doi: 10.1111/micc.12596. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Microcirculation. 2020. PMID: 31628816 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia-induced effects on glycocalyx components in the retina.Exp Eye Res. 2021 Dec;213:108846. doi: 10.1016/j.exer.2021.108846. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Exp Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 34801534 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced expression of junctional adhesion molecule and platelet/endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 (CD31) at human vascular endothelial junctions by cytokines tumor necrosis factor-alpha plus interferon-gamma Does not reduce leukocyte transmigration under flow.Am J Pathol. 2001 Dec;159(6):2281-91. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)63078-7. Am J Pathol. 2001. PMID: 11733377 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 synthesis and leukocyte transmigration in endothelial cells by the combined action of TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma.J Immunol. 1996 Aug 1;157(3):1233-41. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8757631
Cited by
-
Retinal Toxicity Induced by Chemical Agents.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 25;23(15):8182. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158182. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35897758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of Nox4 upregulation on PECAM-1 expression in a mouse model of diabetic retinopathy.PLoS One. 2024 May 15;19(5):e0303010. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303010. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38748682 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Role of Ubiquitination in Eye Diseases.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Sep;82(3):1825-1836. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01381-y. Epub 2024 Jun 24. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38913283 Review.
-
Tocotrienol-rich fraction reduces retinal inflammation and angiogenesis in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023 Jun 2;23(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12906-023-04005-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2023. PMID: 37268913 Free PMC article.
-
Adipose stem cell exosomes, stimulated by pro-inflammatory factors, enhance immune evasion in triple-negative breast cancer by modulating the HDAC6/STAT3/PD-L1 pathway through the transporter UCHL1.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Nov 20;24(1):385. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03557-1. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 39568023 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klein R; Klein BE; Moss SE; Cruickshanks KJ, Relationship of hyperglycemia to the long-term incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy. Arch Intern Med 1994, 154 (19), 2169–78. - PubMed
-
- Leasher JL; Bourne RR; Flaxman SR; Jonas JB; Keeffe J; Naidoo K; Pesudovs K; Price H; White RA; Wong TY; Resnikoff S; Taylor HR; Study, V. L. E. G. o. t. G. B. o. D., Global Estimates on the Number of People Blind or Visually Impaired by Diabetic Retinopathy: A Meta-analysis From 1990 to 2010. Diabetes Care 2016, 39 (9), 1643–9. - PubMed
-
- Antonetti DA; Lieth E; Barber AJ; Gardner TW, Molecular mechanisms of vascular permeability in diabetic retinopathy. Semin Ophthalmol 1999, 14 (4), 240–8. - PubMed
-
- Akram MU; Khalid S; Khan SA, Identification and classification of microaneurysms for early detection of diabetic retinopathy. Pattern Recognition 2013, 46 (1), 107–116.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

