The needle and the haystack: single molecule tracking to probe the transcription factor search in eukaryotes
- PMID: 34003257
- PMCID: PMC8286828
- DOI: 10.1042/BST20200709
The needle and the haystack: single molecule tracking to probe the transcription factor search in eukaryotes
Abstract
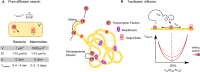
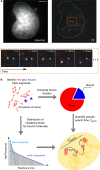
Transcription factors (TFs) regulate transcription of their target genes by identifying and binding to regulatory regions of the genome among billions of potential non-specific decoy sites, a task that is often presented as a 'needle in the haystack' challenge. The TF search process is now well understood in bacteria, but its characterization in eukaryotes needs to account for the complex organization of the nuclear environment. Here we review how live-cell single molecule tracking is starting to shed light on the TF search mechanism in the eukaryotic cell and we outline the future challenges to tackle in order to understand how nuclear organization modulates the TF search process in physiological and pathological conditions.
Keywords: search mechanism; single molecule; transcription factors.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low-Affinity Binding Sites and the Transcription Factor Specificity Paradox in Eukaryotes.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2019 Oct 6;35:357-379. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100617-062719. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2019. PMID: 31283382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How motif environment influences transcription factor search dynamics: Finding a needle in a haystack.Bioessays. 2016 Jul;38(7):605-12. doi: 10.1002/bies.201600005. Epub 2016 May 19. Bioessays. 2016. PMID: 27192961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intra-nuclear mobility and target search mechanisms of transcription factors: a single-molecule perspective on gene expression.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1819(6):482-93. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2012.02.001. Epub 2012 Feb 10. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22342464 Review.
-
Transcription Factor Dynamics: One Molecule at a Time.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Oct 16;39:277-305. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-022823-013847. Epub 2023 Aug 4. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37540844 Review.
-
Capturing the regulatory interactions of eukaryote genomes.Brief Funct Genomics. 2013 Mar;12(2):142-60. doi: 10.1093/bfgp/els041. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Brief Funct Genomics. 2013. PMID: 23117864 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcriptional condensates: a blessing or a curse for gene regulation?Commun Biol. 2024 Feb 16;7(1):187. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-05892-5. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 38365945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How Transcription Factor Clusters Shape the Transcriptional Landscape.Biomolecules. 2024 Jul 20;14(7):875. doi: 10.3390/biom14070875. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39062589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The method in the madness: Transcriptional control from stochastic action at the single-molecule scale.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024 Aug;87:102873. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2024.102873. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2024. PMID: 38954990 Review.
-
Changes in searching behaviour of CSL transcription complexes in Notch active conditions.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 Dec 14;7(3):e202302336. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302336. Print 2024 Mar. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 38097371 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin organization drives the search mechanism of nuclear factors.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 13;14(1):6433. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42133-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37833263 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

