microRNAs: New-Age Panacea in Cancer Therapeutics
- PMID: 33994728
- PMCID: PMC8119568
- DOI: 10.1007/s13193-020-01110-w
microRNAs: New-Age Panacea in Cancer Therapeutics
Abstract
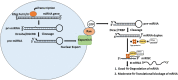
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small (~ 18-25 nucleotides in length), endogenous, non-coding RNAs, which regulate gene expression. Numerous studies have demonstrated the dysregulation of miRNA expression in human cancers through various mechanisms, which include genetic alteration of miRNA genes, abnormal transcriptional control of miRNAs, anomalous epigenetic changes, and defective miRNA biogenesis machinery. They may function as either oncomiRs or tumor suppressor miRNAs in a tissue or cell-specific manner. The dysregulated miRNAs are known to affect the hallmarks of cancer, and some of these miRNAs have shown therapeutic promise in pre-clinical and clinical studies. Here, we briefly touch upon various aspects of miRNA biology with a particular focus on their roles in cancer.
Keywords: Cancer; Clinical trial; Dysregulation; MiRNA.
© Indian Association of Surgical Oncology 2020.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of MicroRNAs in human cancer.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016 Jan 28;1:15004. doi: 10.1038/sigtrans.2015.4. eCollection 2016. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2016. PMID: 29263891 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissecting miRNA facilitated physiology and function in human breast cancer for therapeutic intervention.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Jul;72:46-64. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.05.017. Epub 2020 Jun 1. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 32497683 Review.
-
Recent trends in targeting miRNAs for cancer therapy.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020 Dec;72(12):1732-1749. doi: 10.1111/jphp.13351. Epub 2020 Aug 12. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32783235 Review.
-
Targeting miRNAs and Other Non-Coding RNAs as a Therapeutic Approach: An Update.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Apr 13;9(2):27. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9020027. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 37104009 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Processing and Human Cancer.J Clin Med. 2015 Aug 21;4(8):1651-67. doi: 10.3390/jcm4081651. J Clin Med. 2015. PMID: 26308063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circ_0060967 facilitates proliferation, migration, and invasion of non-small-cell lung cancer cells by sponging miR-660-3p/UBN2.Mol Cell Biochem. 2023 May;478(5):1129-1140. doi: 10.1007/s11010-022-04569-z. Epub 2022 Oct 13. Mol Cell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 36229758
-
LncRNA-MCM3AP-AS1 Promotes the Progression of Infantile Hemangiomas by Increasing miR-138-5p/HIF-1α Axis-Regulated Glycolysis.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Sep 29;8:753218. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.753218. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 34660700 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of microRNAs in septic cardiomyopathy.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jul 5;14:1181372. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1181372. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37475718 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lee RC, Feinbaum RL, Ambros V. The C. elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 1993;75:843–854. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources