Human ribonuclease 1 serves as a secretory ligand of ephrin A4 receptor and induces breast tumor initiation
- PMID: 33986289
- PMCID: PMC8119676
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-23075-2
Human ribonuclease 1 serves as a secretory ligand of ephrin A4 receptor and induces breast tumor initiation
Abstract
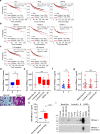
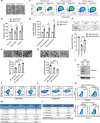
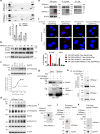
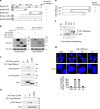
Human ribonuclease 1 (hRNase 1) is critical to extracellular RNA clearance and innate immunity to achieve homeostasis and host defense; however, whether it plays a role in cancer remains elusive. Here, we demonstrate that hRNase 1, independently of its ribonucleolytic activity, enriches the stem-like cell population and enhances the tumor-initiating ability of breast cancer cells. Specifically, secretory hRNase 1 binds to and activates the tyrosine kinase receptor ephrin A4 (EphA4) signaling to promote breast tumor initiation in an autocrine/paracrine manner, which is distinct from the classical EphA4-ephrin juxtacrine signaling through contact-dependent cell-cell communication. In addition, analysis of human breast tumor tissue microarrays reveals a positive correlation between hRNase 1, EphA4 activation, and stem cell marker CD133. Notably, high hRNase 1 level in plasma samples is positively associated with EphA4 activation in tumor tissues from breast cancer patients, highlighting the pathological relevance of the hRNase 1-EphA4 axis in breast cancer. The discovery of hRNase 1 as a secretory ligand of EphA4 that enhances breast cancer stemness suggests a potential treatment strategy by inactivating the hRNase 1-EphA4 axis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Ephrin-A5/EphA4 Interaction Modulates Neurogenesis and Angiogenesis by the p-Akt and p-ERK Pathways in a Mouse Model of TLE.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jan;53(1):561-576. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9020-2. Epub 2014 Dec 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25502292
-
Functional roles of the human ribonuclease A superfamily in RNA metabolism and membrane receptor biology.Mol Aspects Med. 2019 Dec;70:106-116. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Mol Aspects Med. 2019. PMID: 30902663 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ephrin-A1/EphA4-mediated adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1833(10):2201-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.05.017. Epub 2013 May 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23707953
-
LncRNA HOTTIP facilitates the stemness of breast cancer via regulation of miR-148a-3p/WNT1 pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Jun;24(11):6242-6252. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15261. Epub 2020 Apr 19. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32307830 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Potential of EphA4: A Breakthrough Target and Beacon of Hope for Neurological Diseases.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;43(7):3375-3391. doi: 10.1007/s10571-023-01390-0. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37477786 Review.
Cited by
-
Ephs in cancer progression: complexity and context-dependent nature in signaling, angiogenesis and immunity.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 May 29;22(1):299. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01580-3. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38811954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNASE4 promotes malignant progression and chemoresistance in hypoxic glioblastoma via activation of AXL/AKT and NF-κB/cIAPs signaling pathways.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 15;14(9):4320-4336. doi: 10.62347/UDBJ5986. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39417186 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting ALK averts ribonuclease 1-induced immunosuppression and enhances antitumor immunity in hepatocellular carcinoma.Nat Commun. 2024 Feb 2;15(1):1009. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45215-0. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38307859 Free PMC article.
-
Structural insights into EphA4 unconventional activation from prediction of the EphA4 and its complex with ribonuclease 1.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Oct 15;12(10):4865-4878. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36381327 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidation and PEGylation Strategies to Prolong the in Vivo Half-Life of a Nanomolar EphA4 Receptor Antagonist.Eur J Med Chem. 2023 Dec 15;262:115876. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115876. Epub 2023 Oct 16. Eur J Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 38523699 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

