Endothelial SIRT3 regulates myofibroblast metabolic shifts in diabetic kidneys
- PMID: 33981977
- PMCID: PMC8086030
- DOI: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102390
Endothelial SIRT3 regulates myofibroblast metabolic shifts in diabetic kidneys
Abstract
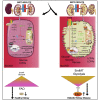
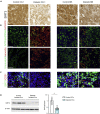
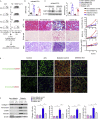
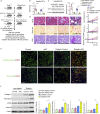
Defects in endothelial cells cause deterioration in kidney function and structure. Here, we found that endothelial SIRT3 regulates metabolic reprogramming and fibrogenesis in the kidneys of diabetic mice. By analyzing, gain of function of the SIRT3 gene by overexpression in a fibrotic mouse strain conferred disease resistance against diabetic kidney fibrosis, whereas its loss of function in endothelial cells exacerbated the levels of diabetic kidney fibrosis. Regulation of endothelial cell SIRT3 on fibrogenic processes was due to tight control over the defective central metabolism and linked activation of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EndMT). SIRT3 deficiency in endothelial cells stimulated the TGFβ/Smad3-dependent mesenchymal transformations in renal tubular epithelial cells. These data demonstrate that SIRT3 regulates defective metabolism and EndMT-mediated activation of the fibrogenic pathways in the diabetic kidneys. Together, our findings show that endothelial SIRT3 is a fundamental regulator of defective metabolism regulating health and disease processes in the kidney.
Keywords: Biological Sciences; Cell Biology; Functional Aspects of Cell Biology.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
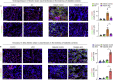
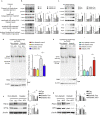
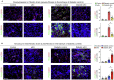
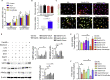
Similar articles
-
Endothelial FGFR1 (Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1) Deficiency Contributes Differential Fibrogenic Effects in Kidney and Heart of Diabetic Mice.Hypertension. 2020 Dec;76(6):1935-1944. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15587. Epub 2020 Nov 2. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 33131311
-
SIRT3 deficiency leads to induction of abnormal glycolysis in diabetic kidney with fibrosis.Cell Death Dis. 2018 Sep 24;9(10):997. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-1057-0. Cell Death Dis. 2018. PMID: 30250024 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition compromises vascular integrity to induce Myc-mediated metabolic reprogramming in kidney fibrosis.Sci Signal. 2020 Jun 9;13(635):eaaz2597. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaz2597. Sci Signal. 2020. PMID: 32518142 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of endothelial-mesenchymal transition in diabetic kidney disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jun;26(12):3313-3322. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17356. Epub 2022 May 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35560773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
microRNA Crosstalk Influences Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal, Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal, and Macrophage-to-Mesenchymal Transitions in the Kidney.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Aug 16;10:904. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00904. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31474862 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic reprogramming: A novel therapeutic target in diabetic kidney disease.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Sep 2;13:970601. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.970601. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36120335 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuins in kidney diseases: potential mechanism and therapeutic targets.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Feb 12;22(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01442-4. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38347622 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirt3 deficiency promotes endothelial dysfunction and aggravates renal injury.PLoS One. 2023 Oct 10;18(10):e0291909. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0291909. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37816025 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting Mitochondrial Sirtuins in Age-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases and Fibrosis.Aging Dis. 2023 Oct 1;14(5):1583-1605. doi: 10.14336/AD.2023.0203. Aging Dis. 2023. PMID: 37196115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Combating Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jul 8;12:716029. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.716029. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34305620 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Cantelmo A.R., Conradi L.C., Brajic A., Goveia J., Kalucka J., Pircher A., Chaturvedi P., Hol J., Thienpont B., Teuwen L.A. Inhibition of the glycolytic activator PFKFB3 in endothelium induces tumor vessel normalization, impairs metastasis, and improves chemotherapy. Cancer Cell. 2016;30:968–985. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen T., Li J., Liu J., Li N., Wang S., Liu H., Zeng M., Zhang Y., Bu P. Activation of SIRT3 by resveratrol ameliorates cardiac fibrosis and improves cardiac function via the TGF-beta/Smad3 pathway. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015;308:H424–H434. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

