Inhibition of the HEG1-KRIT1 interaction increases KLF4 and KLF2 expression in endothelial cells
- PMID: 33977234
- PMCID: PMC8103725
- DOI: 10.1096/fba.2020-00141
Inhibition of the HEG1-KRIT1 interaction increases KLF4 and KLF2 expression in endothelial cells
Abstract
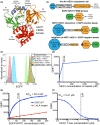
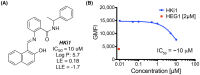
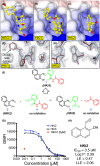
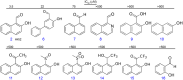
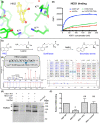
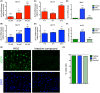
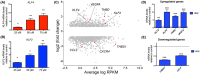
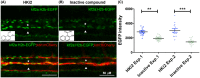
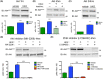
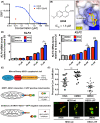
The transmembrane protein heart of glass1 (HEG1) directly binds to and recruits Krev interaction trapped protein 1 (KRIT1) to endothelial junctions to form the HEG1-KRIT1 protein complex that establishes and maintains junctional integrity. Genetic inactivation or knockdown of endothelial HEG1 or KRIT1 leads to the upregulation of transcription factors Krüppel-like factors 4 and 2 (KLF4 and KLF2), which are implicated in endothelial vascular homeostasis; however, the effect of acute inhibition of the HEG1-KRIT1 interaction remains incompletely understood. Here, we report a high-throughput screening assay and molecular design of a small-molecule HEG1-KRIT1 inhibitor to uncover acute changes in signaling pathways downstream of the HEG1-KRIT1 protein complex disruption. The small-molecule HEG1-KRIT1 inhibitor 2 (HKi2) was demonstrated to be a bona fide inhibitor of the interaction between HEG1 and KRIT1 proteins, by competing orthosterically with HEG1 through covalent reversible interactions with the FERM (4.1, ezrin, radixin, and moesin) domain of KRIT1. The crystal structure of HKi2 bound to KRIT1 FERM revealed that it occupies the same binding pocket on KRIT1 as the HEG1 cytoplasmic tail. In human endothelial cells (ECs), acute inhibition of the HEG1-KRIT1 interaction by HKi2 increased KLF4 and KLF2 mRNA and protein levels, whereas a structurally similar inactive compound failed to do so. In zebrafish, HKi2 induced expression of klf2a in arterial and venous endothelium. Furthermore, genome-wide RNA transcriptome analysis of HKi2-treated ECs under static conditions revealed that, in addition to elevating KLF4 and KLF2 expression, inhibition of the HEG1-KRIT1 interaction mimics many of the transcriptional effects of laminar blood flow. Furthermore, HKi2-treated ECs also triggered Akt signaling in a phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K)-dependent manner, as blocking PI3K activity blunted the Akt phosphorylation induced by HKi2. Finally, using an in vitro colocalization assay, we show that HKi6, an improved derivative of HKi2 with higher affinity for KRIT1, significantly impedes recruitment of KRIT1 to mitochondria-localized HEG1 in CHO cells, indicating a direct inhibition of the HEG1-KRIT1 interaction. Thus, our results demonstrate that early events of the acute inhibition of HEG1-KRIT1 interaction with HKi small-molecule inhibitors lead to: (i) elevated KLF4 and KLF2 gene expression; and (ii) increased Akt phosphorylation. Thus, HKi's provide new pharmacologic tools to study acute inhibition of the HEG1-KRIT1 protein complex and may provide insights to dissect early signaling events that regulate vascular homeostasis.
Keywords: HEG1; KLF2; KLF4; KRIT1; endothelial cells.
© 2021 The Authors. FASEB BioAdvances published by the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The structure of the ternary complex of Krev interaction trapped 1 (KRIT1) bound to both the Rap1 GTPase and the heart of glass (HEG1) cytoplasmic tail.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 16;288(33):23639-49. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.462911. Epub 2013 Jun 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23814056 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of the junctional anchorage of the cerebral cavernous malformations complex.J Cell Biol. 2012 Oct 1;199(1):39-48. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201205109. Epub 2012 Sep 24. J Cell Biol. 2012. PMID: 23007647 Free PMC article.
-
Heg1 and Ccm1/2 proteins control endocardial mechanosensitivity during zebrafish valvulogenesis.Elife. 2018 Feb 1;7:e28939. doi: 10.7554/eLife.28939. Elife. 2018. PMID: 29364115 Free PMC article.
-
STRIPAK complexes: structure, biological function, and involvement in human diseases.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014 Feb;47:118-48. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.11.021. Epub 2013 Dec 11. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24333164 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KRIT1: A Traffic Warden at the Busy Crossroads Between Redox Signaling and the Pathogenesis of Cerebral Cavernous Malformation Disease.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Mar;38(7-9):496-528. doi: 10.1089/ars.2021.0263. Epub 2022 Nov 1. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36047808 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein-protein interactions: developing small-molecule inhibitors/stabilizers through covalent strategies.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2023 Jul;44(7):474-488. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2023.04.007. Epub 2023 May 30. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37263826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endothelial Differentiation of CCM1 Knockout iPSCs Triggers the Establishment of a Specific Gene Expression Signature.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 16;24(4):3993. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043993. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835400 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Reversible Covalent Modification of a Noncatalytic Lysine of the Krev Interaction Trapped 1 Protein Enables Site-Directed Screening for Protein-Protein Interaction Inhibitors.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 Oct 9;6(11):1651-1658. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00156. eCollection 2023 Nov 10. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37974623 Free PMC article.
-
Contribution of protein-protein interactions to the endothelial-barrier-stabilizing function of KRIT1.J Cell Sci. 2022 Jan 15;135(2):jcs258816. doi: 10.1242/jcs.258816. Epub 2022 Jan 25. J Cell Sci. 2022. PMID: 34918736 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
