Senescence mechanisms and targets in the heart
- PMID: 33963378
- PMCID: PMC8953446
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvab161
Senescence mechanisms and targets in the heart
Abstract
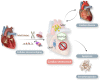
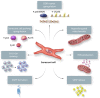
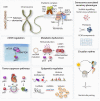
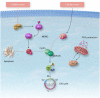
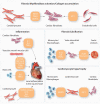
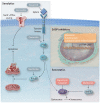
Cellular senescence is a state of irreversible cell cycle arrest associated with ageing. Senescence of different cardiac cell types can direct the pathophysiology of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) such as atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, and cardiac fibrosis. While age-related telomere shortening represents a major cause of replicative senescence, the senescent state can also be induced by oxidative stress, metabolic dysfunction, and epigenetic regulation, among other stressors. It is critical that we understand the molecular pathways that lead to cellular senescence and the consequences of cellular senescence in order to develop new therapeutic approaches to treat CVD. In this review, we discuss molecular mechanisms of cellular senescence, explore how cellular senescence of different cardiac cell types (including cardiomyocytes, cardiac endothelial cells, cardiac fibroblasts, vascular smooth muscle cells, and valve interstitial cells) can lead to CVD, and highlight potential therapeutic approaches that target molecular mechanisms of cellular senescence to prevent or treat CVD.
Keywords: Ageing; Cardiovascular disease; Senescence; Senotherapy.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2021. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of cardiomyocyte senescence in cardiovascular diseases: A molecular biology update.Eur J Pharmacol. 2024 Nov 15;983:176961. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2024.176961. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Eur J Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39209099 Review.
-
Cellular Senescence in Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review.Aging Dis. 2022 Feb 1;13(1):103-128. doi: 10.14336/AD.2021.0927. eCollection 2022 Feb. Aging Dis. 2022. PMID: 35111365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiovascular disease risk factors induce mesenchymal features and senescence in mouse cardiac endothelial cells.Elife. 2021 Mar 4;10:e62678. doi: 10.7554/eLife.62678. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33661096 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular and molecular biology of aging endothelial cells.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015 Dec;89(Pt B):122-35. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2015.01.021. Epub 2015 Feb 2. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015. PMID: 25655936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The roles of senescence and telomere shortening in cardiovascular disease.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013 May;10(5):274-83. doi: 10.1038/nrcardio.2013.30. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23478256 Review.
Cited by
-
A Barth Syndrome Patient-Derived D75H Point Mutation in TAFAZZIN Drives Progressive Cardiomyopathy in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 27;25(15):8201. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158201. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125771 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-7 (IGFBP7) links senescence to heart failure.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Dec;1(12):1195-1214. doi: 10.1038/s44161-022-00181-y. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 39196168 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-203 improves cardiac dysfunction by targeting PARP1-NAD+ axis in aging murine.Aging Cell. 2024 Mar;23(3):e14063. doi: 10.1111/acel.14063. Epub 2023 Dec 14. Aging Cell. 2024. PMID: 38098220 Free PMC article.
-
Diabetes and Its Cardiovascular Complications: Potential Role of the Acetyltransferase p300.Cells. 2023 Jan 28;12(3):431. doi: 10.3390/cells12030431. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36766773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals hub genes of myocardial infarction-associated endothelial cells.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jan 24;24(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03727-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38267885 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang JC, Bennett M. Aging and atherosclerosis: mechanisms, functional consequences, and potential therapeutics for cellular senescence. Circ Res 2012;111:245–259. - PubMed
-
- Das D, Holmes A, Murphy GA, Mishra K, Rosenkranz AC, Horowitz JD, Kennedy JA. TGF-beta1-Induced MAPK activation promotes collagen synthesis, nodule formation, redox stress and cellular senescence in porcine aortic valve interstitial cells. J Heart Valve Dis 2013;22:621–630. - PubMed
-
- Lee J, Termglinchan V, Diecke S, Itzhaki I, Lam CK, Garg P, Lau E, Greenhaw M, Seeger T, Wu H, Zhang JZ, Chen X, Gil IP, Ameen M, Sallam K, Rhee JW, Churko JM, Chaudhary R, Chour T, Wang PJ, Snyder MP, Chang HY, Karakikes I, Wu JC. Activation of PDGF pathway links LMNA mutation to dilated cardiomyopathy. Nature 2019;572:335–340. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chadda KR, Ajijola OA, Vaseghi M, Shivkumar K, Huang CL, Jeevaratnam K. Ageing, the autonomic nervous system and arrhythmia: from brain to heart. Ageing Res Rev 2018;48:40–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

