Metabolic homeostasis via BDNF and its receptors
- PMID: 33958275
- PMCID: PMC8192464
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2021.04.005
Metabolic homeostasis via BDNF and its receptors
Abstract
Metabolic disorders result from dysregulation of central nervous system and peripheral metabolic energy homeostatic pathways. To maintain normal energy balance, neural circuits must integrate feedforward and feedback signals from the internal metabolic environment to orchestrate proper food intake and energy expenditure. These signals include conserved meal and adipocyte cues such as glucose and leptin, respectively, in addition to more novel players including brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). In particular, BDNF's two receptors, tropomyosin related kinase B (TrkB) and p75 neurotrophin receptor (p75NTR), are increasingly appreciated to be involved in whole body energy homeostasis. At times, these two receptors even seem to functionally oppose one another's actions, providing the framework for a potential neurotrophin mediated energy regulatory axis, which we explore further here.
Keywords: BDNF; TrkB; hypothalamus; metabolism; neurotrophins; p75NTR.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests No interests are declared.
Figures
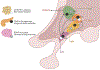
Similar articles
-
The Role of BDNF and TrkB in the Central Control of Energy and Glucose Balance: An Update.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 31;14(4):424. doi: 10.3390/biom14040424. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38672441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Neurotrophic Factor Receptor p75 in the Rat Dorsolateral Striatum Drives Excessive Alcohol Drinking.J Neurosci. 2016 Sep 28;36(39):10116-27. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4597-14.2016. Epub 2016 Sep 28. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27683907 Free PMC article.
-
Circadian control of p75 neurotrophin receptor leads to alternate activation of Nrf2 and c-Rel to reset energy metabolism in astrocytes via brain-derived neurotrophic factor.Free Radic Biol Med. 2018 May 1;119:34-44. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.01.026. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018. PMID: 29374533 Review.
-
The lighter side of BDNF.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 May;300(5):R1053-69. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00776.2010. Epub 2011 Feb 23. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21346243 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TrkB receptor signaling in the nucleus tractus solitarius mediates the food intake-suppressive effects of hindbrain BDNF and leptin.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012 May 1;302(10):E1252-60. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00025.2012. Epub 2012 Feb 28. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2012. PMID: 22374757 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A comprehensive review of genetic causes of obesity.World J Pediatr. 2024 Jan;20(1):26-39. doi: 10.1007/s12519-023-00757-z. Epub 2023 Sep 19. World J Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 37725322 Review.
-
Microbiota-gut-brain axis: the mediator of exercise and brain health.Psychoradiology. 2024 Apr 19;4:kkae007. doi: 10.1093/psyrad/kkae007. eCollection 2024. Psychoradiology. 2024. PMID: 38756477 Free PMC article.
-
Physiological Appetite Regulation and Bariatric Surgery.J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 27;13(5):1347. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051347. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38546831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Leptin Receptor (rs1137101) and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (rs925946) Gene Variants Are Associated with Obesity in the Early- but Not in the Late-Onset Population of Hungarian Psoriatic Patients.Life (Basel). 2021 Oct 14;11(10):1086. doi: 10.3390/life11101086. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34685457 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the effects of BDNF/TRKB signalling on metabolic biomarkers in the liver of sedentary and trained rats with normal and knockout BDNF genotypes.Front Physiol. 2023 Dec 13;14:1268648. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1268648. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 38152248 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morton GJ et al. (2006) Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 443, 289–295 - PubMed
-
- Woods SC et al. (1998) Signals that regulate food intake and energy homeostasis. Science 280, 1378–1383 - PubMed
-
- Lewin GR and Barde YA (1996) Physiology of the neurotrophins. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 19, 289–317 - PubMed
-
- Bibel M and Barde YA (2000) Neurotrophins: key regulators of cell fate and cell shape in the vertebrate nervous system. Genes Dev. 14, 2919–2937 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

