LIFU Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Improving the KCC2 Expression and Inhibiting the CaMKIV-KCC2 Pathway in the L4-L5 Section of the Spinal Cord
- PMID: 33953740
- PMCID: PMC8057881
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6659668
LIFU Alleviates Neuropathic Pain by Improving the KCC2 Expression and Inhibiting the CaMKIV-KCC2 Pathway in the L4-L5 Section of the Spinal Cord
Abstract
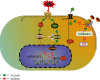
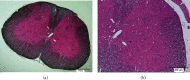
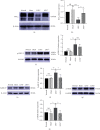
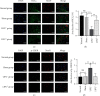
Effective treatment remains lacking for neuropathic pain (NP), a type of intractable pain. Low-intensity focused ultrasound (LIFU), a noninvasive, cutting-edge neuromodulation technique, can effectively enhance inhibition of the central nervous system (CNS) and reduce neuronal excitability. We investigated the effect of LIFU on NP and on the expression of potassium chloride cotransporter 2 (KCC2) in the spinal cords of rats with peripheral nerve injury (PNI) in the lumbar 4-lumbar 5 (L4-L5) section. In this study, rats received PNI surgery on their right lower legs followed by LIFU stimulation of the L4-L5 section of the spinal cord for 4 weeks, starting 3 days after surgery. We used the 50% paw withdraw threshold (PWT50) to evaluate mechanical allodynia. Western blotting (WB) and immunofluorescence (IF) were used to calculate the expression of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (p-ERK1/2), calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV (CaMKIV), phosphorylated cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element-binding protein (p-CREB), and KCC2 in the L4-L5 portion of the spinal cord after the last behavioral tests. We found that PWT50 decreased (P < 0.05) 3 days post-PNI surgery in the LIFU- and LIFU+ groups and increased (P < 0.05) after 4 weeks of LIFU stimulation. The expression of p-CREB and CaMKIV decreased (P < 0.05) and that of KCC2 increased (P < 0.05) after 4 weeks of LIFU stimulation, but that of p-ERK1/2 (P > 0.05) was unaffected. Our study showed that LIFU could effectively alleviate NP behavior in rats with PNI by increasing the expression of KCC2 on spinal dorsal corner neurons. A possible explanation is that LIFU could inhibit the activation of the CaMKIV-KCC2 pathway.
Copyright © 2021 Ye-Hui Liao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Alleviates Spasticity and Increases Expression of the Neuronal K-Cl Cotransporter in the L4-L5 Sections of Rats Following Spinal Cord Injury.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 12;16:882127. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.882127. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35634464 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of Electroacupuncture Intervention on CaMK II-CREB Pathway in Spinal Cord in Rats with Spared Nerve Injury].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2015 Oct;40(5):358-63. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2015. PMID: 26669190 Chinese.
-
Combined use of CLP290 and bumetanide alleviates neuropathic pain and its mechanism after spinal cord injury in rats.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Sep;30(9):e70045. doi: 10.1111/cns.70045. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39267289 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of K+-Cl--Cotransporter-2 in Neuropathic Pain.Neurochem Res. 2018 Jan;43(1):110-115. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2344-3. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 28677029 Review.
-
Therapeutic restoration of spinal inhibition via druggable enhancement of potassium-chloride cotransporter KCC2-mediated chloride extrusion in peripheral neuropathic pain.JAMA Neurol. 2014 May;71(5):640-5. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.21. JAMA Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24615367 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Alleviates Chronic Neuropathic Pain-Induced Allodynia by Inhibiting Neuroplasticity in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex.Neural Plast. 2022 Jul 23;2022:6472475. doi: 10.1155/2022/6472475. eCollection 2022. Neural Plast. 2022. PMID: 35915650 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of the Mechanisms Involved in Neuralgia.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Sep 18;16:4087-4101. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S425966. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37745793 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcranial Ultrasound Stimulation of the Anterior Cingulate Cortex Reduces Neuropathic Pain in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Dec 31;2021:6510383. doi: 10.1155/2021/6510383. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 35003307 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Noninvasive Low-Intensity Focus Ultrasound Neuromodulation on Spinal Cord Neurocircuits In Vivo.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Nov 27;2021:8534466. doi: 10.1155/2021/8534466. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34873411 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Intensity Focused Ultrasound Alleviates Spasticity and Increases Expression of the Neuronal K-Cl Cotransporter in the L4-L5 Sections of Rats Following Spinal Cord Injury.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 12;16:882127. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.882127. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35634464 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

