Type I and III interferon responses in SARS-CoV-2 infection
- PMID: 33953323
- PMCID: PMC8099704
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-021-00592-0
Type I and III interferon responses in SARS-CoV-2 infection
Abstract
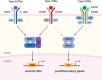
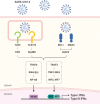
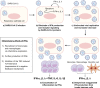
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), the current pandemic disease, is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Type I and III interferons (IFNs) are innate cytokines that are important in the first-line defense against viruses. Similar to many other viruses, SARS-CoV-2 has evolved mechanisms for evading the antiviral effects of type I and III IFNs at multiple levels, including the induction of IFN expression and cellular responses to IFNs. In this review, we describe the innate sensing mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 and the mechanisms used by SARS-CoV-2 to evade type I and III IFN responses. We also discuss contradictory reports regarding impaired and robust type I IFN responses in patients with severe COVID-19. Finally, we discuss how delayed but exaggerated type I IFN responses can exacerbate inflammation and contribute to the severe progression of COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Type I and Type III Interferons - Induction, Signaling, Evasion, and Application to Combat COVID-19.Cell Host Microbe. 2020 Jun 10;27(6):870-878. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.05.008. Epub 2020 May 27. Cell Host Microbe. 2020. PMID: 32464097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antiviral Activity of Type I, II, and III Interferons Counterbalances ACE2 Inducibility and Restricts SARS-CoV-2.mBio. 2020 Sep 10;11(5):e01928-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01928-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32913009 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Evasion of the Interferon System: Can We Restore Its Effectiveness?Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 27;24(11):9353. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119353. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298304 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Antiviral Immune Evasion of SARS-CoV-2.J Mol Biol. 2022 Mar 30;434(6):167265. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167265. Epub 2021 Sep 22. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34562466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protective Potentials of Type III Interferons in COVID-19 Patients: Lessons from Differential Properties of Type I- and III Interferons.Viral Immunol. 2021 Jun;34(5):307-320. doi: 10.1089/vim.2020.0076. Epub 2020 Nov 4. Viral Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33147113 Review.
Cited by
-
After the virus has cleared-Can preclinical models be employed for Long COVID research?PLoS Pathog. 2022 Sep 7;18(9):e1010741. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1010741. eCollection 2022 Sep. PLoS Pathog. 2022. PMID: 36070309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic Mechanisms of the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 and Potential Direct and Indirect Counteractions by Intermittent Fasting.Nutrients. 2022 Dec 21;15(1):20. doi: 10.3390/nu15010020. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36615679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome-mediated delivery of gga-miR-20a-5p regulates immune response of chicken macrophages by targeting IFNGR2, MAPK1, MAP3K5, and MAP3K14.Anim Biosci. 2023 Jun;36(6):851-860. doi: 10.5713/ab.22.0373. Epub 2023 Jan 11. Anim Biosci. 2023. PMID: 36634655 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous Reactions to COVID-19 Vaccines in a Monocentric Study: A Case Series.J Clin Med. 2022 Jun 30;11(13):3811. doi: 10.3390/jcm11133811. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35807096 Free PMC article.
-
Treatments for COVID-19: Lessons from 2020 and new therapeutic options.Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;62:43-59. doi: 10.1016/j.coph.2021.11.002. Epub 2021 Nov 18. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34915400 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

