Atorvastatin Reduces Circulating S100A12 Levels in Patients with Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaques - A Link with Plaque Inflammation
- PMID: 33952812
- PMCID: PMC9135643
- DOI: 10.5551/jat.61630
Atorvastatin Reduces Circulating S100A12 Levels in Patients with Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaques - A Link with Plaque Inflammation
Abstract
Aims: Inflammation is involved in various processes of atherosclerosis development. Serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels, a predictor for cardiovascular risk, are reportedly reduced by statins. However, several studies have demonstrated that CRP is a bystander during atherogenesis. While S100A12 has been focused on as an inflammatory molecule, it remains unclear whether statins affect circulating S100A12 levels. Here, we investigated whether atorvastatin treatment affected S100A12 and which biomarkers were correlated with changes in arterial inflammation.
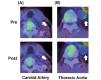
Methods: We performed a prospective, randomized open-labeled trial on whether atorvastatin affected arterial (carotid and thoracic aorta) inflammation using 18fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG-PET/CT) and inflammatory markers. Thirty-one statin-naïve patients with carotid atherosclerotic plaques were randomized to either a group receiving dietary management (n=15) or one receiving atorvastatin (10mg/day, n=16) for 12weeks. 18F-FDG-PET/CT and flow-mediated vasodilation (FMD) were performed, the latter to evaluate endothelial function.
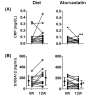
Results: Atorvastatin, but not the diet-only treatment, significantly reduced LDL-cholesterol (LDL-C, -43%), serum CRP (-37%) and S100A12 levels (-28%) and improved FMD (+38%). 18F-FDG-PET/CT demonstrated that atorvastatin, but not the diet-only treatment, significantly reduced accumulation of 18F-FDG in the carotid artery and thoracic aorta. A multivariate analysis revealed that reduction in CRP, S100A12, LDL-C, oxidized-LDL, and increase in FMD were significantly associated with reduced arterial inflammation in the thoracic aorta, but not in the carotid artery.
Conclusions: Atorvastatin treatment reduced S100A12/CRP levels, and the changes in these circulating markers mirrored the improvement in arterial inflammation. Our observations suggest that S100A12 may be an emerging therapeutic target for atherosclerosis.
Keywords: 18F-FDG-PET/CT; Atorvastatin; CRP; Flow-mediated vasodilatation; S100A12.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intensification of statin therapy results in a rapid reduction in atherosclerotic inflammation: results of a multicenter fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography feasibility study.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Sep 3;62(10):909-17. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.04.066. Epub 2013 May 30. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23727083 Clinical Trial.
-
Anti-inflammatory effect of statin is continuously working throughout use: a prospective three time point 18F-FDG PET/CT imaging study.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019 Sep;35(9):1745-1753. doi: 10.1007/s10554-019-01584-y. Epub 2019 Jul 16. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31312997
-
Atorvastatin treatment does not abolish inflammatory mediated cardiovascular risk in subjects with chronic kidney disease.Sci Rep. 2021 Feb 18;11(1):4126. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-83273-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33602971 Free PMC article.
-
A new approach of statin therapy in carotid atherosclerosis: Targeting indices of plaque vulnerability on the top of lipid-lowering. A narrative review.Kardiol Pol. 2022;80(9):880-890. doi: 10.33963/KP.a2022.0155. Epub 2022 Jun 23. Kardiol Pol. 2022. PMID: 35734817 Review.
-
Noninvasive imaging of arterial inflammation using FDG-PET/CT.Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014 Dec;25(6):431-7. doi: 10.1097/MOL.0000000000000135. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2014. PMID: 25340479 Review.
Cited by
-
DBZ (Danshensu Bingpian Zhi), a Novel Natural Compound Derivative, Attenuates Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Deficient Mice.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Oct 2;6(10):e006297. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006297. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28971954 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium Danshensu Inhibits Macrophage Inflammation in Atherosclerosis via the miR-200a-3p/MEKK3/NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov 15. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04626-2. Online ahead of print. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 39546119
-
Adjuvant qi-invigorating blood-activating tongmai decoction promotes effect of rosuvastatin on senile diabetes mellitus complicated with atherosclerosis.Am J Transl Res. 2023 May 15;15(5):3433-3441. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37303639 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Verma S, Szmitko PE and Ridker PM: C-reactive protein comes of age. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med, 2005; 2: 29-36; quiz 58 - PubMed
-
- Koenig W: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein and atherosclerotic disease: from improved risk prediction to risk-guided therapy. Int J Cardiol, 2013; 168: 5126-5134 - PubMed
-
- Ridker PM, Danielson E, Fonseca FA, Genest J, Gotto AM, Jr., Kastelein JJ, Koenig W, Libby P, Lorenzatti AJ, Macfadyen JG, Nordestgaard BG, Shepherd J, Willerson JT and Glynn RJ: Reduction in C-reactive protein and LDL cholesterol and cardiovascular event rates after initiation of rosuvastatin: a prospective study of the JUPITER trial. Lancet, 2009; 373: 1175-1182 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous