Ultrasensitive Detection of p24 in Plasma Samples from People with Primary and Chronic HIV-1 Infection
- PMID: 33952636
- PMCID: PMC8223962
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00016-21
Ultrasensitive Detection of p24 in Plasma Samples from People with Primary and Chronic HIV-1 Infection
Abstract
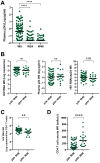
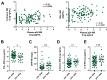
HIV-1 Gag p24 has long been identified as an informative biomarker of HIV replication, disease progression, and therapeutic efficacy, but the lower sensitivity of immunoassays in comparison to molecular tests and the interference with antibodies in chronic HIV infection limit its application for clinical monitoring. The development of ultrasensitive protein detection technologies may help in overcoming these limitations. Here, we evaluated whether immune complex dissociation combined with ultrasensitive digital enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) single-molecule array (Simoa) technology could be used to quantify p24 in plasma samples from people with HIV-1 infection. We found that, among different immune complex dissociation methods, only acid-mediated dissociation was compatible with ultrasensitive p24 quantification by digital ELISA, strongly enhancing p24 detection at different stages of HIV-1 infection. We show that ultrasensitive p24 levels correlated positively with plasma HIV RNA and HIV DNA and negatively with CD4-positive (CD4+) T cells in the samples from people with primary and chronic HIV-1 infection. In addition, p24 levels also correlated with plasma D-dimers and interferon alpha (IFN-α) levels. p24 levels sharply decreased to undetectable levels after initiation of combined antiretroviral treatment (cART). However, we identified a group of people who, 48 weeks after cART initiation, had detectable p24 levels despite most having undetectable viral loads. These people had different virological and immunological baseline characteristics compared with people who had undetectable p24 after cART. These results demonstrate that ultrasensitive p24 analysis provides an efficient and robust means to monitor p24 antigen in plasma samples from people with HIV-1 infection, including during antiretroviral treatment, and may provide complementary information to other commonly used biomarkers. IMPORTANCE The introduction of combined antiretroviral treatment has transformed HIV-1 infection into a manageable condition. In this context, there is a need for additional biomarkers to monitor HIV-1 residual disease or the outcome of new interventions, such as in the case of HIV cure strategies. The p24 antigen has a long half-life outside viral particles, and it is, therefore, a very promising marker to monitor episodes of viral replication or transient activation of the viral reservoir. However, the formation of immune complexes with anti-p24 antibodies makes its quantification difficult beyond acute HIV-1 infection. We show here that, upon immune complex dissociation, new technologies allow the ultrasensitive p24 quantification in plasma samples throughout HIV-1 infection at levels close to those of viral RNA and DNA determinations. Our results further indicate that ultrasensitive p24 quantification may have added value when used in combination with other classic clinical biomarkers.
Keywords: ELISA; Gag p24; HIV p24 antigen; HIV/AIDS; Simoa; biomarker; plasma; plasma marker.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Simple monitoring of antiretroviral therapy with a signal-amplification-boosted HIV-1 p24 antigen assay with heat-denatured plasma.AIDS. 1997 May;11(6):F47-52. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199706000-00001. AIDS. 1997. PMID: 9143600 Clinical Trial.
-
Ultrasensitive HIV-1 p24 Assay Detects Single Infected Cells and Differences in Reservoir Induction by Latency Reversal Agents.J Virol. 2017 Feb 28;91(6):e02296-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02296-16. Print 2017 Mar 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 28077644 Free PMC article.
-
Measurement of HIV-1 p24 antigen by signal-amplification-boosted ELISA of heat-denatured plasma is a simple and inexpensive alternative to tests for viral RNA.AIDS Rev. 2002 Apr-Jun;4(2):83-92. AIDS Rev. 2002. PMID: 12152521 Review.
-
Antiretroviral treatment monitoring with an improved HIV-1 p24 antigen test: an inexpensive alternative to tests for viral RNA.J Med Virol. 2001 Oct;65(2):225-32. doi: 10.1002/jmv.2024. J Med Virol. 2001. PMID: 11536227
-
Viral RNA and p24 antigen as markers of HIV disease and antiretroviral treatment success.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003 Nov;132(3):196-209. doi: 10.1159/000074552. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14646380 Review.
Cited by
-
Developments in Exploring Fungal Secondary Metabolites as Antiviral Compounds and Advances in HIV-1 Inhibitor Screening Assays.Viruses. 2023 Apr 23;15(5):1039. doi: 10.3390/v15051039. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37243125 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assay design for unambiguous identification and quantification of circulating pathogen-derived peptide biomarkers.Theranostics. 2022 Mar 21;12(6):2948-2962. doi: 10.7150/thno.70373. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35401822 Free PMC article.
-
Laboratory-based evaluation of the 4th-generation AlereTM HIV Combo rapid point-of-care test.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 23;19(2):e0298912. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298912. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38394120 Free PMC article.
-
An ultrasensitive planar array p24 Gag ELISA to detect HIV-1 in diverse biological matrixes.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 8;11(1):23682. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03072-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34880361 Free PMC article.
-
Application of ultrasensitive digital ELISA for p24 enables improved evaluation of HIV-1 reservoir diversity and growth kinetics in viral outgrowth assays.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 6;13(1):10958. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37223-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37414788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rutstein SE, Ananworanich J, Fidler S, Johnson C, Sanders EJ, Sued O, Saez-Cirion A, Pilcher CD, Fraser C, Cohen MS, Vitoria M, Doherty M, Tucker JD. 2017. Clinical and public health implications of acute and early HIV detection and treatment: a scoping review. J Int AIDS Soc 20:21579. doi:10.7448/IAS.20.1.21579. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Erikstrup C, Kallestrup P, Zinyama-Gutsire RB, Gomo E, Luneborg-Nielsen M, Gerstoft J, Schupbach J, Ullum H, Katzenstein TL. 2008. p24 as a predictor of mortality in a cohort of HIV-1-infected adults in rural Africa. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr 48:345–349. doi:10.1097/QAI.0b013e31817dc3d1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ledergerber B, Flepp M, Boni J, Tomasik Z, Cone RW, Luthy R, Schupbach J. 2000. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 p24 concentration measured by boosted ELISA of heat-denatured plasma correlates with decline in CD4 cells, progression to AIDS, and survival: comparison with viral RNA measurement. J Infect Dis 181:1280–1288. doi:10.1086/315366. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

