Efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 Covid-19 Vaccine against the B.1.351 Variant
- PMID: 33951374
- PMCID: PMC8091623
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2103055
Efficacy of NVX-CoV2373 Covid-19 Vaccine against the B.1.351 Variant
Abstract
Background: The emergence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants threatens progress toward control of the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic. In a phase 1-2 trial involving healthy adults, the NVX-CoV2373 nanoparticle vaccine had an acceptable safety profile and was associated with strong neutralizing-antibody and antigen-specific polyfunctional CD4+ T-cell responses. Evaluation of vaccine efficacy was needed in a setting of ongoing SARS-CoV-2 transmission.
Methods: In this phase 2a-b trial in South Africa, we randomly assigned human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-negative adults between the ages of 18 and 84 years or medically stable HIV-positive participants between the ages of 18 and 64 years in a 1:1 ratio to receive two doses of either the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine (5 μg of recombinant spike protein with 50 μg of Matrix-M1 adjuvant) or placebo. The primary end points were safety and vaccine efficacy against laboratory-confirmed symptomatic Covid-19 at 7 days or more after the second dose among participants without previous SARS-CoV-2 infection.
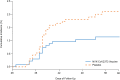
Results: Of 6324 participants who underwent screening, 4387 received at least one injection of vaccine or placebo. Approximately 30% of the participants were seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 at baseline. Among 2684 baseline seronegative participants (94% HIV-negative and 6% HIV-positive), predominantly mild-to-moderate Covid-19 developed in 15 participants in the vaccine group and in 29 in the placebo group (vaccine efficacy, 49.4%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 6.1 to 72.8). Vaccine efficacy among HIV-negative participants was 60.1% (95% CI, 19.9 to 80.1). Of 41 sequenced isolates, 38 (92.7%) were the B.1.351 variant. Post hoc vaccine efficacy against B.1.351 was 51.0% (95% CI, -0.6 to 76.2) among the HIV-negative participants. Preliminary local and systemic reactogenicity events were more common in the vaccine group; serious adverse events were rare in both groups.
Conclusions: The NVX-CoV2373 vaccine was efficacious in preventing Covid-19, with higher vaccine efficacy observed among HIV-negative participants. Most infections were caused by the B.1.351 variant. (Funded by Novavax and the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04533399.).
Copyright © 2021 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Immunogenicity and safety of a SARS-CoV-2 recombinant spike protein nanoparticle vaccine in people living with and without HIV-1 infection: a randomised, controlled, phase 2A/2B trial.Lancet HIV. 2022 May;9(5):e309-e322. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3018(22)00041-8. Lancet HIV. 2022. PMID: 35489376 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Immunogenicity and safety following a homologous booster dose of a SARS-CoV-2 recombinant spike protein vaccine with Matrix-MTM adjuvant (NVX-CoV2373) versus a primary series in people living with and without HIV-1 infection in South Africa: A randomized crossover phase 2a/2b trial.Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024 Dec 31;20(1):2425147. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2024.2425147. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 2024. PMID: 39666396 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety and immunogenicity following a homologous booster dose of a SARS-CoV-2 recombinant spike protein vaccine (NVX-CoV2373): a secondary analysis of a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2022 Nov;22(11):1565-1576. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00420-0. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35963274 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Safety, efficacy, and immunogenicity of the NVX-CoV2373 vaccine.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2023 Jan-Dec;22(1):501-517. doi: 10.1080/14760584.2023.2218913. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2023. PMID: 37246757 Review.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of COVID-19 vaccines in phase III trials: a network meta-analysis.BMC Infect Dis. 2024 Feb 21;24(1):234. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08754-3. BMC Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38383356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
COVID-19 breakthrough infections among people living with and without HIV: A statewide cohort analysis.Int J Infect Dis. 2024 Feb;139:21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2023.11.029. Epub 2023 Nov 25. Int J Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 38013151 Free PMC article.
-
Prospects for durable immune control of SARS-CoV-2 and prevention of reinfection.Nat Rev Immunol. 2021 Jun;21(6):395-404. doi: 10.1038/s41577-021-00550-x. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Nat Rev Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33927374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycoprotein E-Displaying Nanoparticles Induce Robust Neutralizing Antibodies and T-Cell Response against Varicella Zoster Virus.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 12;25(18):9872. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189872. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337359 Free PMC article.
-
Coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine effectiveness among a population-based cohort of people living with HIV.AIDS. 2022 Dec 1;36(15):F17-F26. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000003405. Epub 2022 Oct 19. AIDS. 2022. PMID: 36254892 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2-Specific Vaccine Candidates; the Contribution of Structural Vaccinology.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Feb 3;10(2):236. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10020236. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35214693 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard. https://covid19.who.int/. Accessd December 28, 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it. 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica.... Accessed December 28, 2020.
-
- Le TT, Cramer JP, Chen R, Mayhew S. Evolution of the COVID-19 vaccine development landscape. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2020;19:667–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
