Epstein - Barr virus - encoded microRNAs involve in tumorigenesis and development
- PMID: 33927078
- PMCID: PMC10929937
- DOI: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2021.190744
Epstein - Barr virus - encoded microRNAs involve in tumorigenesis and development
Abstract
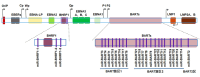
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), a definite tumorigenic virus, is closely related to the development of nasopharyngeal cancer, gastric cancer, lymphoma and other tumors. EBV encodes a total of 44 mature microRNAs, which can regulate the expression of virus and host genes. EBV-encoded microRNAs and their regulated target molecules participate in the biological functions of tumor apoptosis, proliferation, invasion, and metastasis during tumorigenesis and development, and play an important role in the development of tumor.
EB病毒(Epstein-Barr virus,EBV)是一种明确的致瘤性病毒,与鼻咽癌、胃癌、淋巴瘤等多种肿瘤的发生和发展密切相关。EBV共编码44种成熟的微RNA(microRNAs,miRNAs),可调节病毒自身和宿主基因的表达。EBV编码的miRNAs(Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs,EBV miRNAs)及其所调控的靶分子参与肿瘤细胞的凋亡、增殖、侵袭和转移等方面的生物学功能,在肿瘤发生和发展过程中发挥重要作用。.
Keywords: Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; latent infection; tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
作者声称无任何利益冲突。
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded miR-BART6-3p inhibits cancer cell proliferation through the LOC553103-STMN1 axis.FASEB J. 2020 Jun;34(6):8012-8027. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000039RR. Epub 2020 Apr 18. FASEB J. 2020. PMID: 32306460
-
Epstein-Barr Virus MicroRNA miR-BART5-3p Inhibits p53 Expression.J Virol. 2018 Nov 12;92(23):e01022-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01022-18. Print 2018 Dec 1. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 30209170 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus encoded miR-BART11 promotes inflammation-induced carcinogenesis by targeting FOXP1.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 14;7(24):36783-36799. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9170. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27167345 Free PMC article.
-
The oncogenic role of Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinoma.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Jan;22(1):38-45. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13354. Epub 2017 Oct 9. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 28990284 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs as regulators in host immune responses.Int J Biol Sci. 2018 Apr 5;14(5):565-576. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.24562. eCollection 2018. Int J Biol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29805308 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Virus-Induced Host Cell Epigenetic Changes in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 3;22(15):8346. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158346. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34361112 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Epstein MA, Achong BG, Barr YM. Virus Particles in cultured lymphoblasts from Burkitt’s lymphoma[J].Lancet, 1964, 1(7335): 702-703. - PubMed
-
- Dinand V, Sachdeva A, Datta S, et al. . Plasma Epstein Barr virus (EBV) DNA as a biomarker for EBV associated Hodgkin lymphoma[J].Indian Pediatr, 2015, 52(8): 681-685. - PubMed
-
- Hue SSS, Oon ML, Wang S, et al. . Epstein-Barr virus-associated T- and NK-cell lymphoproliferative diseases: an update and diagnostic approach[J].Pathology, 2020, 52(1): 111-127. - PubMed
-
- Kiraz Y, Adan A, Kartal Yandim M, et al. . Major apoptotic mechanisms and genes involved in apoptosis[J].Tumor Biol, 2016, 37(7): 8471-8486. - PubMed
-
- Quintanilla-Martínez L, Lome-Maldonado C, Ott G, et al. . Primary intestinal non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and Epstein-Barr virus: high frequency of EBV-infection in T-cell lymphomas of Mexican origin[J].Leuk Lymphoma, 1998, 30(1/2): 111-121. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources