Activation of the JNK/MAPK Signaling Pathway by TGF-β1 Enhances Neonatal Fc Receptor Expression and IgG Transcytosis
- PMID: 33923917
- PMCID: PMC8073669
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms9040879
Activation of the JNK/MAPK Signaling Pathway by TGF-β1 Enhances Neonatal Fc Receptor Expression and IgG Transcytosis
Abstract
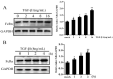
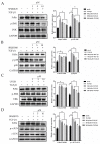
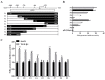
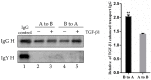
The neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn) transports maternal immunoglobulin G (IgG) to the foetus or newborn and protects the IgG from degradation. FcRn is expressed in several porcine tissues and cell types and its expression levels are regulated by immune and inflammatory events. IPEC-J2 cells are porcine intestinal columnar epithelial cells that were isolated from neonatal piglet mid-jejunum. We hypothesized that transforming growth factor β1 (TGF-β1) upregulated pFcRn expression in IPEC-J2 cells. To test this hypothesis, we treated IPEC-J2 cells with TGF-β1 and demonstrated that porcine FcRn (pFcRn) expression was significantly increased. SP600125, a specific mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) inhibitor, reduced TGF-β1-induced pFcRn expression in IPEC-J2 cells. We performed luciferase reporter assays and showed that the c-JUN sensitive region of the pFcRn promoter gene was located between positions -1215 and -140. The c-JUN sequence, in combination with the pFcRn promoter, regulated luciferase reporter activity in response to TGF-β1 stimulation. Chromatin immunoprecipitation confirmed that there were three c-JUN binding sites in the pFcRn promoter. Furthermore, in addition to increased pFcRn expression, TGF-β1 also enhanced IgG transcytosis in IPEC-J2 cells. In summary, our data showed that the modulation of JNK/MAPK signaling by TGF-β1 was sufficient to upregulate pFcRn expression.
Keywords: JNK pathway; TGF-β1; mucosal immunity; neonatal Fc receptor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TGEV infection up-regulates FcRn expression via activation of NF-κB signaling.Sci Rep. 2016 Aug 24;6:32154. doi: 10.1038/srep32154. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27555521 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal Fc Receptor-Mediated IgG Transport Across Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells: Potentially Provide the Mucosal Protection.DNA Cell Biol. 2016 Jun;35(6):301-9. doi: 10.1089/dna.2015.3165. Epub 2016 Mar 16. DNA Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 26982157
-
TGF-β1 protects intestinal integrity and influences Smads and MAPK signal pathways in IPEC-J2 after TNF-α challenge.Innate Immun. 2017 Apr;23(3):276-284. doi: 10.1177/1753425917690815. Epub 2017 Jan 31. Innate Immun. 2017. PMID: 28142299
-
Transmissible Gastroenteritis Virus Infection Up-Regulates FcRn Expression via Nucleocapsid Protein and Secretion of TGF-β in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells.Front Microbiol. 2020 Jan 21;10:3085. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.03085. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32038538 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and characterization of an alternatively spliced variant of the MHC class I-related porcine neonatal Fc receptor for IgG.Dev Comp Immunol. 2008;32(8):966-79. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2008.01.008. Epub 2008 Feb 20. Dev Comp Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18321573 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The therapeutic age of the neonatal Fc receptor.Nat Rev Immunol. 2023 Jul;23(7):415-432. doi: 10.1038/s41577-022-00821-1. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Nat Rev Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36726033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
"Ways in which the neonatal Fc-receptor is involved in autoimmunity".J Transl Autoimmun. 2021 Sep 11;4:100122. doi: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2021.100122. eCollection 2021. J Transl Autoimmun. 2021. PMID: 34568803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatoprotective Effect of the Penthorum Chinense Pursh Extract against the CCl4-Induced Acute Liver Injury via NF-κB and p38-MAPK PATHWAYS in Dogs.Animals (Basel). 2022 Feb 24;12(5):569. doi: 10.3390/ani12050569. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35268138 Free PMC article.
-
H9N2 Avian Influenza Virus Downregulates FcRY Expression in Chicken Macrophage Cell Line HD11 by Activating the JNK MAPK Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 24;25(5):2650. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052650. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38473897 Free PMC article.
-
1,4-Naphthoquinone Induces FcRn Protein Expression and Albumin Recycling in Human THP-1 Cells.ACS Omega. 2023 Apr 25;8(18):16491-16499. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c01678. eCollection 2023 May 9. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37179634 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ye L., Liu X., Rout S.N., Li Z., Yan Y., Lu L., Kamala T., Nanda N.K., Song W., Samal S.K., et al. The mhc class ii-associated invariant chain interacts with the neonatal fc gamma receptor and modulates its trafficking to endosomal/lysosomal compartments. J. Immunol. (Baltim. Md. 1950) 2008;181:2572–2585. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.4.2572. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li Z., Palaniyandi S., Zeng R., Tuo W., Roopenian D.C., Zhu X. Transfer of igg in the female genital tract by mhc class i-related neonatal fc receptor (fcrn) confers protective immunity to vaginal infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:4388–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012861108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

