RNA-Binding Proteins Hold Key Roles in Function, Dysfunction, and Disease
- PMID: 33923168
- PMCID: PMC8146904
- DOI: 10.3390/biology10050366
RNA-Binding Proteins Hold Key Roles in Function, Dysfunction, and Disease
Abstract
RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are multi-faceted proteins in the regulation of RNA or its RNA splicing, localisation, stability, and translation. Amassing proof from many recent and dedicated studies reinforces the perception of RBPs exerting control through differing expression levels, cellular localization and post-transcriptional alterations. However, since the regulation of RBPs is reliant on the micro-environment and events like stress response and metabolism, their binding affinities and the resulting RNA-RBP networks may be affected. Therefore, any misregulation and disruption in the features of RNA and its related homeostasis can lead to a number of diseases that include diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other disorders such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. As such, correct regulation of RNA and RBPs is crucial to good health as the effect RBPs exert through loss of function can cause pathogenesis. In this review, we will discuss the significance of RBPs and their typical function and how this can be disrupted in disease.
Keywords: RNA binding protein; disease; splicing factor; stress granules; translation regulator.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures
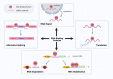
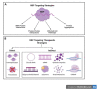
Similar articles
-
Altered mRNP granule dynamics in FTLD pathogenesis.J Neurochem. 2016 Aug;138 Suppl 1:112-33. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13601. Epub 2016 Jun 15. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 26938019 Review.
-
The Emerging Role of the RNA-Binding Protein SFPQ in Neuronal Function and Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 28;21(19):7151. doi: 10.3390/ijms21197151. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32998269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-Binding Proteins in Cancer: Functional and Therapeutic Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 21;12(9):2699. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092699. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32967226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fates and functions of RNA-binding proteins under stress.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Nov 28:e1825. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1825. Online ahead of print. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 38014833 Review.
-
Post-translational Control of RNA-Binding Proteins and Disease-Related Dysregulation.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 27;8:658852. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.658852. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33987205 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeted-Deletion of a Tiny Sequence via Prime Editing to Restore SMN Expression.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 19;23(14):7941. doi: 10.3390/ijms23147941. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35887289 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-binding proteins in bone pathophysiology.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jun 20;12:1412268. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1412268. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38966428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RNA-Binding Proteins as Critical Post-Transcriptional Regulators of Cardiac Regeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 26;24(15):12004. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512004. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proximity-dependent biotinylation technologies for mapping RNA-protein interactions in live cells.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Nov 14;9:1062448. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1062448. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36452457 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in the study of RNA-binding proteins in diabetic complications.Mol Metab. 2022 Aug;62:101515. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2022.101515. Epub 2022 May 18. Mol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35597446 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

