MRCKα Is Dispensable for Breast Cancer Development in the MMTV-PyMT Model
- PMID: 33921698
- PMCID: PMC8073694
- DOI: 10.3390/cells10040942
MRCKα Is Dispensable for Breast Cancer Development in the MMTV-PyMT Model
Abstract
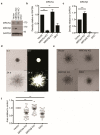
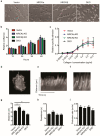
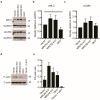
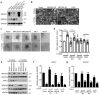
MRCKα is a ubiquitously expressed serine/threonine kinase involved in cell contraction and F-actin turnover, which is highly amplified in human breast cancer and part of a gene expression signature for bad prognosis. Nothing is known about the in vivo function of MRCKα. To explore MRCKα function in development and in breast cancer, we generated mice lacking a functional MRCKα gene. Mice were born close to the Mendelian ratio and showed no obvious phenotype including a normal mammary gland formation. Assessing breast cancer development using the transgenic MMTV-PyMT mouse model, loss of MRCKα did not affect tumor onset, tumor growth and metastasis formation. Deleting MRCKα and its related family member MRCKβ in two triple-negative breast cancer cell lines resulted in reduced invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells, but did not affect migration of 4T1 cells. Further genomic analysis of human breast cancers revealed that MRCKα is frequently co-amplified with the oncogenes ARID4B and AKT3 which might contribute to the prognostic value of MRCKα expression. Collectively, these data suggest that MRCKα might be a prognostic marker for breast cancer, but probably of limited functional importance.
Keywords: MRCK; breast cancer; invasion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deletion of Col15a1 Modulates the Tumour Extracellular Matrix and Leads to Increased Tumour Growth in the MMTV-PyMT Mouse Mammary Carcinoma Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Sep 15;22(18):9978. doi: 10.3390/ijms22189978. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34576139 Free PMC article.
-
Frequent overexpression of AMAP1, an Arf6 effector in cell invasion, is characteristic of the MMTV-PyMT rather than the MMTV-Neu human breast cancer model.Cell Commun Signal. 2018 Jan 5;16(1):1. doi: 10.1186/s12964-017-0212-z. Cell Commun Signal. 2018. PMID: 29329590 Free PMC article.
-
Zhuidu Formula suppresses the migratory and invasive properties of triple-negative breast cancer cells via dual signaling pathways of RhoA/ROCK and CDC42/MRCK.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Oct 28;315:116644. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116644. Epub 2023 May 16. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37196814
-
MMTV mouse models and the diagnostic values of MMTV-like sequences in human breast cancer.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009 Jul;9(5):423-40. doi: 10.1586/erm.09.31. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009. PMID: 19580428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opportunities and Challenges for the Development of MRCK Kinases Inhibitors as Potential Cancer Chemotherapeutics.Cells. 2023 Feb 7;12(4):534. doi: 10.3390/cells12040534. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831201 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Rho family GTPase signaling through type II p21-activated kinases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Nov 19;79(12):598. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04618-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36401658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MRCK activates mouse oocyte myosin II for spindle rotation and male pronucleus centration.J Cell Biol. 2023 Nov 6;222(11):e202211029. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202211029. Epub 2023 Aug 31. J Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 37651121 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Unbekandt M., Belshaw S., Bower J., Clarke M., Cordes J., Crighton D., Croft D.R., Drysdale M.J., Garnett M.J., Gill K., et al. Discovery of Potent and Selective MRCK Inhibitors with Therapeutic Effect on Skin Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018;78:2096–2114. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-2870. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

