The Hallmarks of Flavonoids in Cancer
- PMID: 33918290
- PMCID: PMC8038160
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26072029
The Hallmarks of Flavonoids in Cancer
Abstract
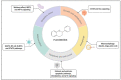
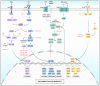
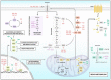
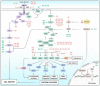
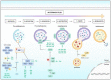
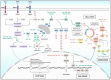
Flavonoids represent an important group of bioactive compounds derived from plant-based foods and beverages with known biological activity in cells. From the modulation of inflammation to the inhibition of cell proliferation, flavonoids have been described as important therapeutic adjuvants against several diseases, including diabetes, arteriosclerosis, neurological disorders, and cancer. Cancer is a complex and multifactor disease that has been studied for years however, its prevention is still one of the best known and efficient factors impacting the epidemiology of the disease. In the molecular and cellular context, some of the mechanisms underlying the oncogenesis and the progression of the disease are understood, known as the hallmarks of cancer. In this text, we review important molecular signaling pathways, including inflammation, immunity, redox metabolism, cell growth, autophagy, apoptosis, and cell cycle, and analyze the known mechanisms of action of flavonoids in cancer. The current literature provides enough evidence supporting that flavonoids may be important adjuvants in cancer therapy, highlighting the importance of healthy and balanced diets to prevent the onset and progression of the disease.
Keywords: cancer; cell signaling; flavonoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fisetin and Quercetin: Promising Flavonoids with Chemopreventive Potential.Biomolecules. 2019 May 6;9(5):174. doi: 10.3390/biom9050174. Biomolecules. 2019. PMID: 31064104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beneficial action of Citrus flavonoids on multiple cancer-related biological pathways.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007 Dec;7(8):795-809. doi: 10.2174/156800907783220435. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2007. PMID: 18220529 Review.
-
Targeting Inflammation by Flavonoids: Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Metabolic Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 8;20(19):4957. doi: 10.3390/ijms20194957. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31597283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent Insights into Therapeutic Potential of Plant-Derived Flavonoids against Cancer.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022;22(20):3343-3369. doi: 10.2174/1871520622666220421094055. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35593353 Review.
-
Flavonoids Alleviating Insulin Resistance through Inhibition of Inflammatory Signaling.J Agric Food Chem. 2019 May 15;67(19):5361-5373. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05348. Epub 2019 Jan 22. J Agric Food Chem. 2019. PMID: 30612424 Review.
Cited by
-
Endoplasmic reticulum as a target in cardiovascular diseases: Is there a role for flavonoids?Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 10;13:1027633. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1027633. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36703744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AfCHIL, a Type IV Chalcone Isomerase, Enhances the Biosynthesis of Naringenin in Metabolic Engineering.Front Plant Sci. 2022 May 18;13:891066. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.891066. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35665193 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Fisetin in Selected Malignant Neoplasms in Women.Nutrients. 2023 Nov 5;15(21):4686. doi: 10.3390/nu15214686. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37960338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antioxidants in brain tumors: current therapeutic significance and future prospects.Mol Cancer. 2022 Oct 28;21(1):204. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01668-9. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36307808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of a Concoction of Natural Bioactive Compounds-Mechanistic Insights.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 22;9(11):1522. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9111522. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34829751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

