Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells as a Tool to Investigate the Effects of Cyanidin 3- O-Glucoside on Cell Differentiation
- PMID: 33916494
- PMCID: PMC8038597
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073768
Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells as a Tool to Investigate the Effects of Cyanidin 3- O-Glucoside on Cell Differentiation
Abstract
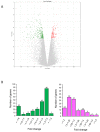
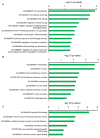
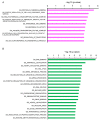
Cyanidin, a kind of anthocyanin, has been reported to have chemotherapeutic activities in humans. Human amniotic epithelial cells (hAECs) are considered a potential source of pluripotent stem cells. hAECs have been used as a novel tool in regenerative cellular therapy and cell differentiation studies. In this study, to explore the effects of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside (Cy3G) on hAECs and their mechanisms, we investigated the transcriptomic changes in the Cy3G-treated cells using microarray analysis. Among the differentially expressed genes (Fold change > 1.1; p-value < 0.05), 109 genes were upregulated and 232 were downregulated. Ratios of upregulated and downregulated genes were 0.22% and 0.47% of the total expressed genes, respectively. Next, we explored the enriched gene ontology, i.e., the biological process, molecular function, and cellular component of the 37 upregulated (>1.3-fold change) and 124 downregulated (<1.3-fold change) genes. Significantly enriched biological processes by the upregulated genes included "response to muscle activity," and the genes involved in this gene ontology (GO) were Metrnl and SRD5A1, which function in the adipocyte. On the other hand, the cell cycle biological process was significantly enriched by the downregulated genes, including some from the SMC gene family. An adipogenesis-associated gene DDX6 was also included in the cell cycle biological process. Thus, our findings suggest the prospects of Cy3G in modulating adipocyte differentiation in hAECs.
Keywords: adipocyte; amniotic epithelial cells; cell differentiation; cyanidin-3-O-glucoside; global gene expression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cyanidin-3-glucoside derived from black soybeans ameliorate type 2 diabetes through the induction of differentiation of preadipocytes into smaller and insulin-sensitive adipocytes.J Nutr Biochem. 2015 Aug;26(8):860-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Apr 23. J Nutr Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25940979
-
Regulating cell fate of human amnion epithelial cells using natural compounds: an example of enhanced neural and pigment differentiation by 3,4,5-tri-O-caffeoylquinic acid.Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Feb 24;19(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00697-5. Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33627134 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of epidermal growth factor on the proliferation and cell cycle regulation of cultured human amnion epithelial cells.J Biosci Bioeng. 2012 Aug;114(2):220-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2012.03.021. Epub 2012 May 10. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012. PMID: 22578596
-
Stem cell characteristics and the therapeutic potential of amniotic epithelial cells.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2018 Oct;80(4):e13003. doi: 10.1111/aji.13003. Epub 2018 Jun 29. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29956869 Review.
-
Human amniotic membrane as an alternative source of stem cells for regenerative medicine.Differentiation. 2011 Mar;81(3):162-71. doi: 10.1016/j.diff.2011.01.005. Epub 2011 Feb 19. Differentiation. 2011. PMID: 21339039 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulating Early Biological Events in Human Amniotic Epithelial Stem Cells Using Natural Bioactive Compounds: Extendable Multidirectional Research Avenues.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Apr 1;10:865810. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.865810. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35433672 Free PMC article.
-
Maize Flavonoid Biosynthesis, Regulation, and Human Health Relevance: A Review.Molecules. 2022 Aug 13;27(16):5166. doi: 10.3390/molecules27165166. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36014406 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High serum levels of L-carnitine and citric acid negatively correlated with alkaline phosphatase are detectable in Koreans before gastric cancer onset.Metabolomics. 2022 Jul 28;18(8):62. doi: 10.1007/s11306-022-01922-7. Metabolomics. 2022. PMID: 35900644
-
Effects of Isorhamnetin on Diabetes and Its Associated Complications: A Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies and a Post Hoc Transcriptome Analysis of Involved Molecular Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 9;23(2):704. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020704. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Descriptive Whole-Genome Transcriptomics Study in a Stem Cell-Based Tool Predicts Multiple Tissue-Specific Beneficial Potential and Molecular Targets of Carnosic Acid.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 29;24(9):8077. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098077. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175790 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matsukawa T., Inaguma T., Han J., Villareal M.O., Isoda H. Cyanidin-3-glucoside derived from black soybeans ameliorate type 2 diabetes through the induction of differentiation of preadipocytes into smaller and insulin-sensitive adipocytes. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015;26:860–867. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.03.006. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

