Anti-Angiogenic Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
- PMID: 33916438
- PMCID: PMC8038573
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22073765
Anti-Angiogenic Therapy: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives
Abstract
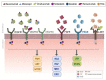
Anti-angiogenic therapy is an old method to fight cancer that aims to abolish the nutrient and oxygen supply to the tumor cells through the decrease of the vascular network and the avoidance of new blood vessels formation. Most of the anti-angiogenic agents approved for cancer treatment rely on targeting vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) actions, as VEGF signaling is considered the main angiogenesis promotor. In addition to the control of angiogenesis, these drugs can potentiate immune therapy as VEGF also exhibits immunosuppressive functions. Despite the mechanistic rational that strongly supports the benefit of drugs to stop cancer progression, they revealed to be insufficient in most cases. We hypothesize that the rehabilitation of old drugs that interfere with mechanisms of angiogenesis related to tumor microenvironment might represent a promising strategy. In this review, we deepened research on the molecular mechanisms underlying anti-angiogenic strategies and their failure and went further into the alternative mechanisms that impact angiogenesis. We concluded that the combinatory targeting of alternative effectors of angiogenic pathways might be a putative solution for anti-angiogenic therapies.
Keywords: VEGF; anti-angiogenic therapy; cancer therapy; drug resistance; neo-angiogenesis; new targets.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose any conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting tumor micro-environment for design and development of novel anti-angiogenic agents arresting tumor growth.Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013 Nov;113(2):333-54. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2013.10.001. Epub 2013 Oct 15. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24139944 Review.
-
Role of the microenvironment in tumor growth and in refractoriness/resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies.Drug Resist Updat. 2008 Dec;11(6):219-30. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2008.09.001. Epub 2008 Oct 23. Drug Resist Updat. 2008. PMID: 18948057 Review.
-
Anti-Angiogenics: Current Situation and Future Perspectives.Oncol Res Treat. 2018;41(4):166-171. doi: 10.1159/000488087. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Oncol Res Treat. 2018. PMID: 29562226 Review.
-
Direct Effects of Anti-Angiogenic Therapies on Tumor Cells: VEGF Signaling.Trends Mol Med. 2017 Mar;23(3):282-292. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.01.002. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Trends Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28162910 Review.
-
Targeting Angiogenesis in Cancer Therapy: Moving Beyond Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor.Oncologist. 2015 Jun;20(6):660-73. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2014-0465. Epub 2015 May 22. Oncologist. 2015. PMID: 26001391 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive compounds isolated from the bark of Aesculus glabra Willd.Phytochem Lett. 2024 Jun;61:106-114. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2024.04.005. Epub 2024 Apr 12. Phytochem Lett. 2024. PMID: 39479302
-
Integrated metabolomics and transcriptomics analysis reveals the mechanism of Tangbi capsule for diabetic lower extremities arterial disease.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 22;15:1423428. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1423428. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39104587 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of the efficacy and safety of anlotinib for the treatment of recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer.Discov Oncol. 2024 Aug 29;15(1):383. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01267-8. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39207632 Free PMC article.
-
Personalized functional profiling using ex-vivo patient-derived spheroids points out the potential of an antiangiogenic treatment in a patient with a metastatic lung atypical carcinoid.Cancer Biol Ther. 2022 Dec 31;23(1):96-102. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2021.2021042. Cancer Biol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35193475 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of the T2 Ribonucleases in TME-Based Cancer Therapy.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 1;11(8):2160. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082160. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Domingues G., Fernandes S.G., Serpa J. Understand Cancer: Research and Treatment. iConcept Press; Hong Kong, China: 2015. Dynamics of VEGF-A and its Receptors in Cancer Vascularization—An Overview. Chapter 3.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

