Effect of O-linked glycosylation on the antigenicity, cellular uptake and trafficking in dendritic cells of recombinant Ber e 1
- PMID: 33914740
- PMCID: PMC8084162
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0249876
Effect of O-linked glycosylation on the antigenicity, cellular uptake and trafficking in dendritic cells of recombinant Ber e 1
Abstract
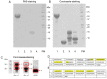
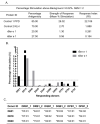
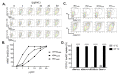
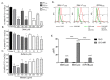
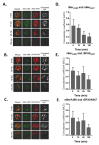
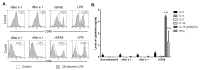
Ber e 1, a major Brazil nut allergen, has been successfully produced in the yeast Pichia pastoris expression system as homogenous recombinant Ber e 1 (rBer e 1) with similar physicochemical properties and identical immunoreactivity to its native counterpart, nBer e 1. However, O-linked glycans was detected on the P.pastoris-derived rBer e 1, which is not naturally present in nBer e 1, and may contribute to the allergic sensitisation. In this study, we addressed the glycosylation differences between P. pastoris-derived recombinant Ber e 1 and its native counterparts. We also determined whether this fungal glycosylation could affect the antigenicity and immunogenicity of the rBer e 1 by using dendritic cells (DC) as an immune cell model due to their role in modulating the immune response. We identified that the glycosylation occurs at Ser96, Ser101 and Ser110 on the large chain and Ser19 on the small polypeptide chain of rBer e 1 only. The glycosylation on rBer e 1 was shown to elicit varying degree of antigenicity by binding to different combination of human leukocyte antigens (HLA) at different frequencies compared to nBer e 1 when tested using human DC-T cell assay. However, both forms of Ber e 1 are weak immunogens based from their low response indexes (RI). Glycans present on rBer e 1 were shown to increase the efficiency of the protein recognition and internalization by murine bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (bmDC) via C-type lectin receptors, particularly the mannose receptor (MR), compared to the non-glycosylated nBer e 1 and SFA8, a weak allergenic 2S albumin protein from sunflower seed. Binding of glycosylated rBer e 1 to MR alone was found to not induce the production of IL-10 that modulates bmDC to polarise Th2 cell response by suppressing IL-12 production and DC maturation. Our findings suggest that the O-linked glycosylation by P. pastoris has a small but measurable effect on the in vitro antigenicity of the rBer e 1 compared to its non-glycosylated counterpart, nBer e 1, and thus may influence its applications in diagnostics and immunotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential polarization of immune responses by plant 2S seed albumins, Ber e 1, and SFA8.J Immunol. 2006 Aug 1;177(3):1561-6. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.177.3.1561. J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16849463
-
N-glycosylation converts non-glycoproteins into mannose receptor ligands and reveals antigen-specific T cell responses in vivo.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 24;8(4):6857-6872. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14314. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28036287 Free PMC article.
-
The dendritic cell mannose receptor mediates allergen internalization and maturation involving notch 1 signalling.Clin Exp Immunol. 2010 Nov;162(2):251-61. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2010.04244.x. Epub 2010 Sep 1. Clin Exp Immunol. 2010. PMID: 20819091 Free PMC article.
-
Ber e 1 protein: the versatile major allergen from Brazil nut seeds.Biotechnol Lett. 2012 Apr;34(4):597-610. doi: 10.1007/s10529-011-0831-1. Epub 2011 Dec 21. Biotechnol Lett. 2012. PMID: 22187079 Review.
-
Proposed mechanism of off-target toxicity for antibody-drug conjugates driven by mannose receptor uptake.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013 Feb;62(2):217-23. doi: 10.1007/s00262-012-1369-3. Epub 2012 Dec 8. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2013. PMID: 23223907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Allergic Inflammation: Effect of Propolis and Its Flavonoids.Molecules. 2022 Oct 8;27(19):6694. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196694. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235230 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Menz G, Dolecek C, Ferreira F, Moser M, Suter T, M S, et al.. Serological and skin-test diagnosis of bireh pollen allergy with recombinant Bet v I, the major birch pollen allergen. Clin Exp Allergy. 1996;26(26):50–60. - PubMed
-
- Ree R Van, Leeuwen WA Van, Akkerdaas JH, Aalberse RC. How far can we simplify in vitro diagnostics for Fagales tree pollen allergy? A study with three whole pollen extracts and purified natural and recombinant allergens. Clin Exp Allergy. 1999;29:848–55. 10.1046/j.1365-2222.1999.00521.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

