Identification of a prognostic long noncoding RNA signature in lung squamous cell carcinoma: a population-based study with a mean follow-up of 3.5 years
- PMID: 33910626
- PMCID: PMC8082628
- DOI: 10.1186/s13690-021-00588-2
Identification of a prognostic long noncoding RNA signature in lung squamous cell carcinoma: a population-based study with a mean follow-up of 3.5 years
Abstract
Background: Lung squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) is a form of cancer that is associated with high rates of relapse, poor responsiveness to therapy, and a relatively poor prognosis. The relationship between long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) expression and LSCC patient prognosis remains to be established.
Methods: In the present study, we discovered that lncRNAs were differentially expressed in LSCC tumor tissues relative to normal control tissues, and we explored the prognostic relevance of these lncRNA expression patterns using data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA).
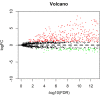
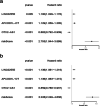
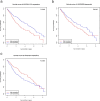
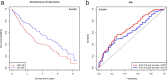
Results: These multidimensional data were analyzed in order to identify lncRNA signatures that were associated with LSCC patient survival outcomes. Kaplan-Meier survival curves revealed prognostic capabilities for three of these lncRNAs (LINC02555, APCDD1L-DT and OTX2-AS1). A Cox regression analysis revealed this three-lncRNA signature to be significantly associated with patient survival. Further GO and KEGG analyses revealed that the predicted target genes of these three lncRNAs were also potentially involved in cancer-associated pathways.
Conclusions: Together these results thus indicate that this novel three-lncRNA signature can be used to predict LSCC patient prognosis.
Keywords: LncRNAs; Lung squamous cell carcinoma; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An immune-related lncRNA pairs signature to identify the prognosis and predict the immune landscape of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 May 14;22(1):545. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09524-1. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35568824 Free PMC article.
-
The Prognostic Signature and Potential Target Genes of Six Long Non-coding RNA in Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Genet. 2020 Apr 28;11:413. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00413. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2020. PMID: 32411183 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a five-long non-coding RNA signature to improve the prognosis prediction for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Aug 14;24(30):3426-3439. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i30.3426. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30122881 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a progression-associated long non-coding RNA signature for predicting the prognosis of lung squamous cell carcinoma.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Feb;15(2):1185-1192. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.5571. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 29434705 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the oral cancer lncRNAome: Identification of novel lncRNAs associated with malignant progression and HPV infection.Oral Oncol. 2016 Aug;59:58-66. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.05.014. Oral Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27424183 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of cuproptosis-related lncRNAs signature for predicting the prognosis in patients with kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024 Mar;22(1):100338. doi: 10.1016/j.jgeb.2023.100338. Epub 2024 Jan 30. J Genet Eng Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38494257 Free PMC article.
-
A Signature of 14 Long Non-Coding RNAs (lncRNAs) as a Step towards Precision Diagnosis for NSCLC.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 16;14(2):439. doi: 10.3390/cancers14020439. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35053601 Free PMC article.
-
A novel pyroptosis-related lncRNA prognostic signature associated with the immune microenvironment in lung squamous cell carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2022 Jun 23;22(1):694. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-09790-z. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35739504 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of pyroptosis-related long non-coding RNAs with prognosis and therapy in lung squamous cell carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 1;12(1):11206. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15373-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35778526 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value and immunological characteristics of a novel cuproptosis-related long noncoding RNAs risk signature in kidney renal clear cell carcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Nov 3;13:1009555. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.1009555. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 36406128 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS executive committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165(2):277–304. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.165.2.ats01. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mayer JE, Swetter SM, Fu T, Geller AC. Screening, early detection, education, and trends for melanoma: current status (2007–2013) and future directions: Part II. Screening, education, and future directions. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71(4):611.e1–611.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2014.05.045. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Travis WD, Brambilla E, Noguchi M, Nicholson AG, Geisinger KR, Yatabe Y, Beer DG, Powell CA, Riely GJ, van Schil PE, Garg K, Austin JHM, Asamura H, Rusch VW, Hirsch FR, Scagliotti G, Mitsudomi T, Huber RM, Ishikawa Y, Jett J, Sanchez-Cespedes M, Sculier JP, Takahashi T, Tsuboi M, Vansteenkiste J, Wistuba I, Yang PC, Aberle D, Brambilla C, Flieder D, Franklin W, Gazdar A, Gould M, Hasleton P, Henderson D, Johnson B, Johnson D, Kerr K, Kuriyama K, Lee JS, Miller VA, Petersen I, Roggli V, Rosell R, Saijo N, Thunnissen E, Tsao M, Yankelewitz D. International association for the study of lung cancer/american thoracic society/european respiratory society international multidisciplinary classification of lung adenocarcinoma. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6(2):244–285. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e318206a221. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

