Prognostic value of SH3PXD2B (Tks4) in human hepatocellular carcinoma: a combined multi-omics and experimental study
- PMID: 33906640
- PMCID: PMC8080318
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-021-00963-6
Prognostic value of SH3PXD2B (Tks4) in human hepatocellular carcinoma: a combined multi-omics and experimental study
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most common and fatal cancers worldwide. HCC invasion and metastasis are crucial for its poor prognosis. SH3PXD2B is a scaffold protein and critical for intravascular and extravascular invasion and metastasis of various types of tumors. However, the role of SH3PXD2B in HCC progression remains unclear.
Methods: The levels of SH3PXD2B mRNA transcripts in the TCGA database and SH3PXD2B protein expression in the Human Protein Atlas were analyzed. Furthermore, the levels of SH3PXD2B expression in clinical samples were analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. The potential association of the levels of SH3PXD2B expression with clinicopathological characteristics, overall survival (OS), and recurrence-free survival (RFS) of HCC patients was analyzed. The impact of SH3PXD2B silencing by shRNA-based lentivirus transduction on the proliferation and invasion of human HCC Hep3B and Huh7 cells was determined.
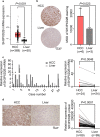
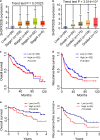
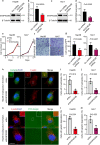
Results: SH3PXD2B expression was up-regulated in HCC tissues in the TCGA and Human Protein Atlas as well as clinical samples, relative to that of non-tumor liver samples. The levels of SH3PXD2B expression in HCC tissues were significantly associated with higher HBV infection rate, higher HCC grades and TNM stages, higher Ki-67 expression, higher serum α-fetoprotein (AFP), a shorter OS and RFS of HCC patients. Functionally, SH3PXD2B silencing significantly inhibited the formation and function of invadopodia and the invasion of Hep3B and Huh7 cells, but did not affect their proliferation in vitro.
Conclusions: Our data suggest that SH3PXD2B may promote the invasion and metastasis of HCC and be a valuable therapeutic target and biomarker for treatment and prognosis of HCC.
Keywords: Clinicopathology; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Human Protein Atlas; Invasion; Omics; Proliferation; Recurrence; SH3PXD2B; Survival; TCGA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A novel prognostic biomarker SPC24 up-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2015 Dec 1;6(38):41383-97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5510. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26515591 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of long non-coding RNA MALAT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: A study based on multi-omics analysis and RT-PCR validation.Pathol Oncol Res. 2023 Jan 4;28:1610808. doi: 10.3389/pore.2022.1610808. eCollection 2022. Pathol Oncol Res. 2023. PMID: 36685103 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of CDCA5 inhibits cancer progression and serves as a prognostic biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2018 Oct;40(4):1875-1884. doi: 10.3892/or.2018.6579. Epub 2018 Jul 17. Oncol Rep. 2018. PMID: 30015982 Free PMC article.
-
Glypican-3 is a biomarker and a therapeutic target of hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015 Aug;14(4):361-6. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(15)60396-4. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2015. PMID: 26256079 Review.
-
The role of RNA modifications in hepatocellular carcinoma: functional mechanism and potential applications.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 20;15:1439485. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1439485. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39229278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
miR-647 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell progression by targeting protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type F.Bioengineered. 2022 Jan;13(1):1090-1102. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2017628. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 34969357 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of Scaffold Protein Tks4 Disrupts Several Signaling Pathways in Colon Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 9;24(2):1310. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021310. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36674824 Free PMC article.
-
A diagnostic circulating miRNA signature as orchestrator of cell invasion via TKS4/TKS5/EFHD2 modulation in human gliomas.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Mar 17;42(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02639-8. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 36932446 Free PMC article.
-
Correspondence to editorial on "Multiomics profiling of buffy coat and plasma unveils etiology-specific signatures in hepatocellular carcinoma".Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024 Oct;30(4):1009-1011. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2024.0368. Epub 2024 May 20. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38768961 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Unveiling epithelial plasticity regulation in lung cancer: Exploring the cross-talk among Tks4 scaffold protein partners.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Aug 1;35(8):ar111. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-03-0103. Epub 2024 Jul 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38985526 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ke Y, Wu T, Lei X, Zhang C, Zhou J, Li J, Zhang H, Chen X, Wang J, Wang L. Reduced glutathione ameliorates liver function, oxidative stress and inflammation after interventional therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J BUON. 2020;25(3):1361–1367. - PubMed
-
- Ke Y, Zhong J, Guo Z, Liang Y, Li L, Xiang B. Comparison liver resection with transarterial chemoembolization for Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage B hepatocellular carcinoma patients on long-term survival after SPSS propensity score matching. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2014;94(10):747–750. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Ke Y, Lei X, Wu T, Li Y, Bao T, Tang H, Zhang C, Wu X, Wang G, et al. Meta-analysis: the efficacy of metformin and other anti-hyperglycemic agents in prolonging the survival of hepatocellular carcinoma patients with type 2 diabetes. Ann Hepatol. 2020;19(3):320–328. doi: 10.1016/j.aohep.2019.11.008. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

