Human ALKBH6 Is Required for Maintenance of Genomic Stability and Promoting Cell Survival During Exposure of Alkylating Agents in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 33897761
- PMCID: PMC8058185
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2021.635808
Human ALKBH6 Is Required for Maintenance of Genomic Stability and Promoting Cell Survival During Exposure of Alkylating Agents in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
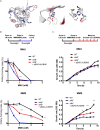
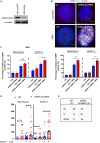
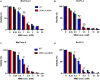
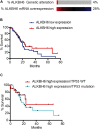
Alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase (ALKBH) is a DNA repair gene involved in the repair of alkylating DNA damage. There are nine types of ALKBH (ALKBH1-8 and FTO) identified in humans. In particular, certain types of ALKBH enzymes are dioxygenases that directly reverse DNA methylation damage via transfer of a methyl group from the DNA adduct onto α-ketoglutarate and release of metabolic products including succinate and formaldehyde. Here, we tested whether ALKBH6 plays a significant role in preventing alkylating DNA damage and decreasing genomic instability in pancreatic cancer cells. Using an E. coli strain deficient with ALKB, we found that ALKBH6 complements ALKB deficiency and increases resistance after alkylating agent treatment. In particular, the loss of ALKBH6 in human pancreatic cancer cells increases alkylating agent-induced DNA damage and significantly decreases cell survival. Furthermore, in silico analysis from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database suggests that overexpression of ALKBH6 provides better survival outcomes in patients with pancreatic cancer. Overall, our data suggest that ALKBH6 is required to maintain the integrity of the genome and promote cell survival of pancreatic cancer cells.
Keywords: Alkb E. coli; DNA repair; alkbh6; alkylating DNA damage; pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2021 Zhao, Devega, Francois and Kidane.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel AlkB dioxygenases--alternative models for in silico and in vivo studies.PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30588. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030588. Epub 2012 Jan 24. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22291995 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Characterization of a Putative RNA Demethylase ALKBH6 in Arabidopsis Growth and Abiotic Stress Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 13;21(18):6707. doi: 10.3390/ijms21186707. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32933187 Free PMC article.
-
Oncometabolite D-2-Hydroxyglutarate Inhibits ALKBH DNA Repair Enzymes and Sensitizes IDH Mutant Cells to Alkylating Agents.Cell Rep. 2015 Dec 22;13(11):2353-2361. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2015.11.029. Epub 2015 Dec 10. Cell Rep. 2015. PMID: 26686626 Free PMC article.
-
Dealkylation of Macromolecules by Eukaryotic α-Ketoglutarate-Dependent Dioxygenases from the AlkB-like Family.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 20;46(9):10462-10491. doi: 10.3390/cimb46090622. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39329974 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The AlkB Family of Fe(II)/α-Ketoglutarate-dependent Dioxygenases: Repairing Nucleic Acid Alkylation Damage and Beyond.J Biol Chem. 2015 Aug 21;290(34):20734-20742. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R115.656462. Epub 2015 Jul 7. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26152727 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor-Associated Inflammation: The Tumor-Promoting Immunity in the Early Stages of Tumorigenesis.J Immunol Res. 2022 Jun 13;2022:3128933. doi: 10.1155/2022/3128933. eCollection 2022. J Immunol Res. 2022. PMID: 35733919 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of demethylase AlkB homologs in cancer.Front Oncol. 2023 Mar 16;13:1153463. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1153463. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37007161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phylogenetic and functional analyses of N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation factors in the wheat scab fungus Fusarium graminearum.mSphere. 2024 Jan 30;9(1):e0055223. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00552-23. Epub 2023 Dec 12. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 38085094 Free PMC article.
-
Human APOE ɛ3 and APOE ɛ4 Alleles Have Differential Effects on Mouse Olfactory Epithelium.J Alzheimers Dis. 2022;85(4):1481-1494. doi: 10.3233/JAD-215152. J Alzheimers Dis. 2022. PMID: 34958025 Free PMC article.
-
ALKBH4 impedes 5-FU Sensitivity through suppressing GSDME induced pyroptosis in gastric cancer.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jun 20;15(6):435. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06832-1. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38902235 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

