Immunomodulatory Effects of Dopamine in Inflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 33897712
- PMCID: PMC8063048
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.663102
Immunomodulatory Effects of Dopamine in Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
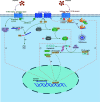
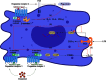
Dopamine (DA) receptor, a significant G protein-coupled receptor, is classified into two families: D1-like (D1 and D5) and D2-like (D2, D3, and D4) receptor families, with further formation of homodimers, heteromers, and receptor mosaic. Increasing evidence suggests that the immune system can be affected by the nervous system and neurotransmitters, such as dopamine. Recently, the role of the DA receptor in inflammation has been widely studied, mainly focusing on NLRP3 inflammasome, NF-κB pathway, and immune cells. This article provides a brief review of the structures, functions, and signaling pathways of DA receptors and their relationships with inflammation. With detailed descriptions of their roles in Parkinson disease, inflammatory bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and multiple sclerosis, this article provides a theoretical basis for drug development targeting DA receptors in inflammatory diseases.
Keywords: Parkinson disease; dopamine; inflammation; inflammatory bowel disease; multiple sclerosis; rheumatoid arthritis; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2021 Feng and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The modulatory role of dopamine receptors in brain neuroinflammation.Int Immunopharmacol. 2019 Nov;76:105908. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105908. Epub 2019 Oct 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31622861 Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects Mediated by Dopamine.J Immunol Res. 2016;2016:3160486. doi: 10.1155/2016/3160486. Epub 2016 Oct 4. J Immunol Res. 2016. PMID: 27795960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The peripheral dopaminergic system: morphological analysis, functional and clinical applications.Ital J Anat Embryol. 2002 Jul-Sep;107(3):145-67. Ital J Anat Embryol. 2002. PMID: 12437142 Review.
-
Roles of dopamine receptor subtypes in mediating modulation of T lymphocyte function.Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2010;31(6):782-91. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2010. PMID: 21196914
-
Dopamine receptors - IUPHAR Review 13.Br J Pharmacol. 2015 Jan;172(1):1-23. doi: 10.1111/bph.12906. Br J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25671228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating serotonin and dopamine concentrations in osteoarthritis patients: a pilot study on the effect of pelotherapy.Int J Biometeorol. 2024 Jan;68(1):69-77. doi: 10.1007/s00484-023-02571-8. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Int J Biometeorol. 2024. PMID: 37962646 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Dopamine Receptors on Osteoblasts as a Possible Therapeutic Strategy for Inducing Bone Formation in Arthritis.Cells. 2022 May 11;11(10):1609. doi: 10.3390/cells11101609. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35626646 Free PMC article.
-
Olanzapine's effects on hypothalamic transcriptomics and kinase activity.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2024 May;163:106987. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2024.106987. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2024. PMID: 38340539
-
Cannabidiol's neuroprotective properties and potential treatment of traumatic brain injuries.Front Neurol. 2023 Feb 2;14:1087011. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1087011. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36816569 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variation in the Dopamine-4-Receptor Gene in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes.Neuroendocrinology. 2023;113(8):875-884. doi: 10.1159/000530765. Epub 2023 Apr 20. Neuroendocrinology. 2023. PMID: 37080173 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

