Isochorismatase domain-containing protein 1 (ISOC1) participates in DNA damage repair and inflammation-related pathways to promote lung cancer development
- PMID: 33889521
- PMCID: PMC8044495
- DOI: 10.21037/tlcr-21-219
Isochorismatase domain-containing protein 1 (ISOC1) participates in DNA damage repair and inflammation-related pathways to promote lung cancer development
Abstract
Background: The advent of novel molecular targets has dramatically changed the treatment landscape of lung cancer in recent years. Isochorismatase domain-containing protein 1 (ISOC1) has been reported as a potential biomarker in gastrointestinal cancer, while its function in lung cancer has not been determined.
Methods: The expression levels and prognostic significance of ISOC1 were assessed using bioinformatic analysis. Overexpression of ISOC1 and miR-4633, and knockdown of ISOC1 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines were generated by lentiviral infection with overexpressed or shRNA plasmids. CRISPR/Cas9 system was applied to knockout ISOC1 in A549 cells. The functions of ISOC1 and miR-4633 in lung cancer development were investigated using cell proliferation, migration, and invasion assays. Xenograft tumor growth assays in nude mice were further assessed the effect of ISOC1 in the tumorigenesis of NSCLC in vivo. Cell cycle distribution analysis was performed to uncover the underlying mechanism of ISOC1 and miR-4633 in promoting NSCLC cell proliferation. Co-immunoprecipitation combined with mass spectrometry and RNA sequencing were performed to uncover the potential mechanism of ISOC1 in lung cancer development.
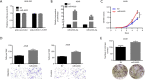
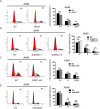
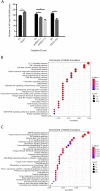
Results: Our results found that ISOC1 expression was upregulated in NSCLC tissues and that increased expression of ISOC1 was significantly associated with worse disease-free survival in NSCLC patients. Overexpression of ISOC1 could increase the proliferation, viability, migration, and invasion of NSCLC cells. Furthermore, miR-4633, located in the first intron of ISOC1, could also promote tumor cell progression and metastasis. Mice xenograft tumor assay showed that knockout of ISOC1 could significantly inhibit tumor growth in vivo. Besides, co-immunoprecipitation combined with mass spectrometry assay revealed that ISOC1 interacted with the proteins of DNA damage repair pathways and that upregulated ISOC1 expression could significantly increase the number of DNA damage lesions. RNA sequencing analysis showed that the downstream signaling pathways mediated by ISOC1 were mainly inflammation-related.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that ISOC1 and its intronic miR-4633, both of them could promote NSCLC cell proliferation, migration, invasion, and cell cycle progression. ISOC1 participates in DNA damage repair and inflammation to promote lung cancer development.
Keywords: DNA damage repair; Isochorismatase domain-containing protein 1 (ISOC1); inflammation; lung cancer; miR-4633.
2021 Translational Lung Cancer Research. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at http://dx.doi.org/10.21037/tlcr-21-219). Dr. JM has served on the Advisory Board of Astra Zeneca and Blueprint Medicines. The authors have no other conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Knockdown of ISOC1 inhibits the proliferation and migration and induces the apoptosis of colon cancer cells through the AKT/GSK-3β pathway.Carcinogenesis. 2020 Aug 12;41(8):1123-1133. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgz188. Carcinogenesis. 2020. PMID: 31740942 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of ISOC1 suppresses cell proliferation in pancreatic cancer in vitro.Oncol Lett. 2019 May;17(5):4263-4270. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10082. Epub 2019 Feb 28. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 30944620 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-330-3p promotes cell invasion and metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer through GRIA3 by activating MAPK/ERK signaling pathway.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jun 19;10(1):125. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0493-0. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. Retraction in: J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Oct 22;13(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00969-0 PMID: 28629431 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
ISOC1 is a novel potential tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma.Neoplasma. 2022 Jan;69(1):174-182. doi: 10.4149/neo_2021_210815N1157. Epub 2021 Nov 30. Neoplasma. 2022. PMID: 34846160
-
LncRNA PKMYT1AR promotes cancer stem cell maintenance in non-small cell lung cancer via activating Wnt signaling pathway.Mol Cancer. 2021 Dec 2;20(1):156. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01469-6. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34856993 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
High Expression of circ_0001821 Promoted Colorectal Cancer Progression Through miR-600/ISOC1 Axis.Biochem Genet. 2023 Feb;61(1):410-427. doi: 10.1007/s10528-022-10262-z. Epub 2022 Aug 9. Biochem Genet. 2023. PMID: 35943670 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Secreted Proteins from Prepubertal Ovarian Tissues Exposed In Vitro to Cisplatin and LH.Cells. 2022 Apr 3;11(7):1208. doi: 10.3390/cells11071208. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406774 Free PMC article.
-
Selpercatinib and capmatinib combination promotes sustained complete response in novel ISOC1-RET fusion lung cancer after resistance to RET inhibitor via MET amplification: Case Report.Front Oncol. 2023 Oct 9;13:1264231. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1264231. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37876974 Free PMC article.
-
Ten Years of CRISPRing Cancers In Vitro.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Nov 23;14(23):5746. doi: 10.3390/cancers14235746. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36497228 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ISOC1 Modulates Inflammatory Responses in Macrophages through the AKT1/PEX11B/Peroxisome Pathway.Molecules. 2022 Sep 11;27(18):5896. doi: 10.3390/molecules27185896. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36144632 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
