Hypercholesterolemia and related risk factors in a cohort of patients with diabetes and hypertension in Maputo, Mozambique
- PMID: 33889268
- PMCID: PMC8035689
- DOI: 10.11604/pamj.2021.38.102.27284
Hypercholesterolemia and related risk factors in a cohort of patients with diabetes and hypertension in Maputo, Mozambique
Abstract
Introduction: some studies reported that 25.5% of African population presents hypercholesterolemia; however, epidemiology of hypercholesterolemia in Africa is poorly described. Mozambique is experiencing a constant growth of non-communicable diseases, but scarce data are available about hypercholesterolemia. Our study aims at describing the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia in patients with diabetes and hypertension in Mozambique and investigate possible risk factors.
Methods: we conducted a cross-sectional study involving all the patients diagnosed with hypertension and/or diabetes from June 2018 to November 2020 in the Zimpeto DREAM Centre (Maputo, Mozambique). For each patient, anthropometric, clinical and laboratory data were collected. Hypercholesterolemia was defined as total blood cholesterol >200 mg/dL. Univariable and multivariable analysis were perfumed.
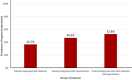
Results: a total of 885 patients were included, 76.2% (n=674) female. Hypertension alone was diagnosed in 670 (75.7%) patients, diabetes in 109 (12.3%) patients and 106 (11.9%) both diseases. Hypercholesterolemia was present in 410 (46.3%) patients and it was more prevalent in patients diagnosed with both diabetes and hypertension (52.8%), as compared to the patients diagnosed with hypertension (46.9%) or diabetes alone (36.7%). In the multivariable analysis, the only factors independently associated with hypercholesterolemia were female sex (aOR 1.77, 95% CI 1.26-2.48, p=0.001) and a body mass index >25kg/m2 (aOR 1.50, 95% CI 1.11-2.04, p=0.008).
Conclusion: our results highlight the need for a specific focus on female and obese/overweight patients, especially if diagnosed with both hypertension and diabetes, to promptly detect metabolic disorders and establish temporary preventive measures for cardiovascular events.
Keywords: Hypercholesterolemia; cardiovascular risk factor; non-communicable diseases.
Copyright: Fausto Ciccacci et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Clustering of cardiometabolic risk factors in sub-Saharan Africans.Pan Afr Med J. 2021 Feb 3;38:112. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.38.112.28180. eCollection 2021. Pan Afr Med J. 2021. PMID: 33912282 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Awareness, treatment, and control of major cardiovascular risk factors in a small-scale Italian community: results of a screening campaign.Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2013;9:177-85. doi: 10.2147/VHRM.S40925. Epub 2013 Apr 30. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2013. PMID: 23662063 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of non-communicable diseases and associated risk factors amongst adults living with HIV in Cambodia.PLoS One. 2017 Nov 9;12(11):e0187591. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0187591. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 29121661 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Obesity and Its Association with Undiagnosed Diabetes Mellitus, High Blood Pressure and Hypercholesterolemia in the Malaysian Adult Population: A National Cross-Sectional Study Using NHMS Data.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Feb 9;20(4):3058. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20043058. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36833764 Free PMC article.
-
Multicentric study on prevalence and risk factors for hypertension and diabetes in tribal communities in Western and Northern Maharashtra.J Postgrad Med. 2018 Jan-Mar;64(1):23-34. doi: 10.4103/jpgm.JPGM_245_17. J Postgrad Med. 2018. PMID: 29386415 Free PMC article.
-
Social determinants and behaviors associated with overweight and obesity among youth and adults in a peri-urban area of Maputo City, Mozambique.J Glob Health. 2021 Mar 27;11:04021. doi: 10.7189/jogh.11.04021. J Glob Health. 2021. PMID: 33868672 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The effect of results-based motivating system on metabolic risk factors of non-communicable diseases: A field trial study.PLoS One. 2024 Oct 17;19(10):e0311507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0311507. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39418251 Free PMC article.
-
Processed food consumption and risk of non-communicable diseases (NCDs) in South Africa: evidence from Demographic and Health Survey (DHS) VII.J Nutr Sci. 2024 Mar 27;13:e19. doi: 10.1017/jns.2024.13. eCollection 2024. J Nutr Sci. 2024. PMID: 38572366 Free PMC article.
-
Implementing HbA1c monitoring in sub-Saharan Africa: Lessons learnt from a pilot project in Mozambique.Public Health Pract (Oxf). 2024 May 16;7:100504. doi: 10.1016/j.puhip.2024.100504. eCollection 2024 Jun. Public Health Pract (Oxf). 2024. PMID: 38840715 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering of cardiometabolic risk factors in sub-Saharan Africans.Pan Afr Med J. 2021 Feb 3;38:112. doi: 10.11604/pamj.2021.38.112.28180. eCollection 2021. Pan Afr Med J. 2021. PMID: 33912282 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Determinants of Dyslipidemia in Africa: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Feb 23;8:778891. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.778891. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35284497 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Mean cholesterol - global health observatory (GHO) data. 2020.
-
- Noubiap JJ, Bigna JJ, Nansseu JR, Nyaga UF, Balti EV, Echouffo-Tcheugui JB, et al. Prevalence of dyslipidaemia among adults in Africa: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6(9):e998–e1007. - PubMed
-
- Kassa M, Grace J. Public Health in Developing Countries-Challenges and Opportunities: IntechOpen. 2019. The global burden and perspectives on non-communicable diseases (NCDs) and the prevention, data availability and systems approach of NCDs in low- resource countries.
-
- Gouda HN, Charlson F, Sorsdahl K, Ahmadzada S, Ferrari AJ, Erskine H, et al. Burden of non-communicable diseases in sub-Saharan Africa, 1990-2017: results from the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(10):e1375–e87. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical