BAP1 constrains pervasive H2AK119ub1 to control the transcriptional potential of the genome
- PMID: 33888563
- PMCID: PMC8091973
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.347005.120
BAP1 constrains pervasive H2AK119ub1 to control the transcriptional potential of the genome
Abstract
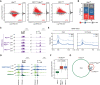
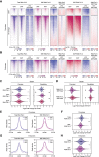
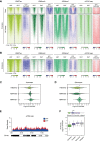
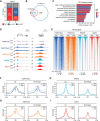
Histone-modifying systems play fundamental roles in gene regulation and the development of multicellular organisms. Histone modifications that are enriched at gene regulatory elements have been heavily studied, but the function of modifications found more broadly throughout the genome remains poorly understood. This is exemplified by histone H2A monoubiquitylation (H2AK119ub1), which is enriched at Polycomb-repressed gene promoters but also covers the genome at lower levels. Here, using inducible genetic perturbations and quantitative genomics, we found that the BAP1 deubiquitylase plays an essential role in constraining H2AK119ub1 throughout the genome. Removal of BAP1 leads to pervasive genome-wide accumulation of H2AK119ub1, which causes widespread reductions in gene expression. We show that elevated H2AK119ub1 preferentially counteracts Ser5 phosphorylation on the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II at gene regulatory elements and causes reductions in transcription and transcription-associated histone modifications. Furthermore, failure to constrain pervasive H2AK119ub1 compromises Polycomb complex occupancy at a subset of Polycomb target genes, which leads to their derepression, providing a potential molecular rationale for why the BAP1 ortholog in Drosophila has been characterized as a Polycomb group gene. Together, these observations reveal that the transcriptional potential of the genome can be modulated by regulating the levels of a pervasive histone modification.
Keywords: BAP1; H2AK119ub1; Polycomb; chromatin; deubiquitylase; epigenetics; gene expression; histone modification; histone monoubiquitylation; transcription.
© 2021 Fursova et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PR-DUB safeguards Polycomb repression through H2AK119ub1 restriction.Cell Prolif. 2023 Oct;56(10):e13457. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13457. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36959757 Free PMC article.
-
BAP1 enhances Polycomb repression by counteracting widespread H2AK119ub1 deposition and chromatin condensation.Mol Cell. 2021 Sep 2;81(17):3526-3541.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.06.020. Epub 2021 Jun 28. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 34186021 Free PMC article.
-
PR-DUB maintains the expression of critical genes through FOXK1/2- and ASXL1/2/3-dependent recruitment to chromatin and H2AK119ub1 deubiquitination.Genome Res. 2020 Aug;30(8):1119-1130. doi: 10.1101/gr.261016.120. Epub 2020 Aug 3. Genome Res. 2020. PMID: 32747411 Free PMC article.
-
Functional Link between BRCA1 and BAP1 through Histone H2A, Heterochromatin and DNA Damage Response.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016;16(2):101-9. doi: 10.2174/1568009615666151030102427. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2016. PMID: 26517537 Review.
-
Polycomb-dependent histone H2A ubiquitination links developmental disorders with cancer.Trends Genet. 2022 Apr;38(4):333-352. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2021.07.011. Epub 2021 Aug 20. Trends Genet. 2022. PMID: 34426021 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis of histone H2A lysine 119 deubiquitination by Polycomb Repressive Deubiquitinase BAP1/ASXL1.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 23:2023.02.23.529554. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.23.529554. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Sci Adv. 2023 Aug 9;9(32):eadg9832. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adg9832 PMID: 36865140 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Modulation of Schwann cell homeostasis by the BAP1 deubiquitinase.Glia. 2023 Jun;71(6):1466-1480. doi: 10.1002/glia.24351. Epub 2023 Feb 15. Glia. 2023. PMID: 36790040 Free PMC article.
-
PR-DUB safeguards Polycomb repression through H2AK119ub1 restriction.Cell Prolif. 2023 Oct;56(10):e13457. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13457. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Cell Prolif. 2023. PMID: 36959757 Free PMC article.
-
The N-terminal region of DNMT3A engages the nucleosome surface to aid chromatin recruitment.EMBO Rep. 2024 Dec;25(12):5743-5779. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00306-3. Epub 2024 Nov 11. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 39528729 Free PMC article.
-
Human ASXL1-Mutant Hematopoiesis Is Driven by a Truncated Protein Associated with Aberrant Deubiquitination of H2AK119.Blood Cancer Discov. 2024 May 1;5(3):202-223. doi: 10.1158/2643-3230.BCD-23-0235. Blood Cancer Discov. 2024. PMID: 38359087 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
