Insights into SARS-CoV-2: Medicinal Chemistry Approaches to Combat Its Structural and Functional Biology
- PMID: 33886017
- PMCID: PMC8061463
- DOI: 10.1007/s41061-021-00335-9
Insights into SARS-CoV-2: Medicinal Chemistry Approaches to Combat Its Structural and Functional Biology
Abstract
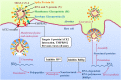
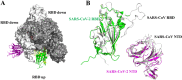
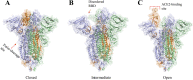
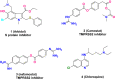
Coronavirus disease 2019, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is still a pandemic around the world. Currently, specific antiviral drugs to control the epidemic remain deficient. Understanding the details of SARS-CoV-2 structural biology is extremely important for development of antiviral agents that will enable regulation of its life cycle. This review focuses on the structural biology and medicinal chemistry of various key proteins (Spike, ACE2, TMPRSS2, RdRp and Mpro) in the life cycle of SARS-CoV-2, as well as their inhibitors/drug candidates. Representative broad-spectrum antiviral drugs, especially those against the homologous virus SARS-CoV, are summarized with the expectation they will drive the development of effective, broad-spectrum inhibitors against coronaviruses. We are hopeful that this review will be a useful aid for discovery of novel, potent anti-SARS-CoV-2 drugs with excellent therapeutic results in the near future.
Keywords: Antiviral; COVID-19; Drug discovery; SARS-CoV-2; Structural biology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
An Updated Review on Betacoronavirus Viral Entry Inhibitors: Learning from Past Discoveries to Advance COVID-19 Drug Discovery.Curr Top Med Chem. 2021;21(7):571-596. doi: 10.2174/1568026621666210119111409. Curr Top Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33463470 Review.
-
The Repurposed ACE2 Inhibitors: SARS-CoV-2 Entry Blockers of Covid-19.Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021 Oct 8;379(6):40. doi: 10.1007/s41061-021-00353-7. Top Curr Chem (Cham). 2021. PMID: 34623536 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contributions of human ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in determining host-pathogen interaction of COVID-19.J Genet. 2021;100(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s12041-021-01262-w. J Genet. 2021. PMID: 33707363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential therapeutic approaches for the early entry of SARS-CoV-2 by interrupting the interaction between the spike protein on SARS-CoV-2 and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2).Biochem Pharmacol. 2021 Oct;192:114724. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2021.114724. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Biochem Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34371003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between ACE2 and SARS-CoV-2 S Protein: Peptide Inhibitors for Potential Drug Developments Against COVID-19.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021;22(10):729-744. doi: 10.2174/1389203722666210916141924. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2021. PMID: 34530706 Review.
Cited by
-
Activity of a Carbohydrate-Binding Module Therapy, Neumifil, against SARS-CoV-2 Disease in a Hamster Model of Infection.Viruses. 2022 May 6;14(5):976. doi: 10.3390/v14050976. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35632718 Free PMC article.
-
Development of Fluorescence-Based Assays for Key Viral Proteins in the SARS-CoV-2 Infection Process and Lifecycle.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 1;25(5):2850. doi: 10.3390/ijms25052850. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38474097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress on COVID-19 Chemotherapeutics Discovery and Novel Technology.Molecules. 2022 Nov 26;27(23):8257. doi: 10.3390/molecules27238257. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36500347 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of Inhibitory Activity In Silico of In-House Thiomorpholine Compounds between the ACE2 Receptor and S1 Subunit of SARS-CoV-2 Spike.Pathogens. 2021 Sep 17;10(9):1208. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10091208. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 34578240 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
