Correlation of [18F]florbetaben textural features and age of onset of Alzheimer's disease: a principal components analysis approach
- PMID: 33881633
- PMCID: PMC8060386
- DOI: 10.1186/s13550-021-00774-x
Correlation of [18F]florbetaben textural features and age of onset of Alzheimer's disease: a principal components analysis approach
Abstract
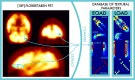
Background: When Alzheimer's disease (AD) is occurring at an early onset before 65 years old, its clinical course is generally more aggressive than in the case of a late onset. We aim at identifying [[Formula: see text]F]florbetaben PET biomarkers sensitive to differences between early-onset Alzheimer's disease (EOAD) and late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD). We conducted [[Formula: see text]F]florbetaben PET/CT scans of 43 newly diagnosed AD subjects. We calculated 93 textural parameters for each of the 83 Hammers areas. We identified 41 independent principal components for each brain region, and we studied their Spearman correlation with the age of AD onset, by taking into account multiple comparison corrections. Finally, we calculated the probability that EOAD and LOAD patients have different amyloid-[Formula: see text] ([Formula: see text]) deposition by comparing the mean and the variance of the significant principal components obtained in the two groups with a 2-tailed Student's t-test.
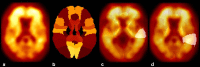
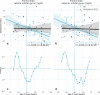
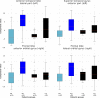
Results: We found that four principal components exhibit a significant correlation at a 95% confidence level with the age of onset in the left lateral part of the anterior temporal lobe, the right anterior orbital gyrus of the frontal lobe, the right lateral orbital gyrus of the frontal lobe and the left anterior part of the superior temporal gyrus. The data are consistent with the hypothesis that EOAD patients have a significantly different [[Formula: see text]F]florbetaben uptake than LOAD patients in those four brain regions.
Conclusions: Early-onset AD implies a very irregular pattern of [Formula: see text] deposition. The authors suggest that the identified textural features can be used as quantitative biomarkers for the diagnosis and characterization of EOAD patients.
Keywords: Early-onset Alzheimer’s disease; Positron emission tomography; Textural analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-invasive quantification of 18F-florbetaben with total-body EXPLORER PET.EJNMMI Res. 2024 Apr 16;14(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01104-7. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 38625413 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid deposition in early onset versus late onset Alzheimer's disease.J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;35(4):813-21. doi: 10.3233/JAD-121927. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013. PMID: 23507771
-
Regional Comparison of Imaging Biomarkers in the Striatum between Early- and Late-onset Alzheimer's Disease.Exp Neurobiol. 2022 Dec 31;31(6):401-408. doi: 10.5607/en22022. Exp Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 36631848 Free PMC article.
-
Critical role of mitosis in spontaneous late-onset Alzheimer's disease; from a Shugoshin 1 cohesinopathy mouse model.Cell Cycle. 2018;17(19-20):2321-2334. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2018.1515554. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Cell Cycle. 2018. PMID: 30231670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[(18)F]Florbetaben: a review in β-amyloid PET imaging in cognitive impairment.CNS Drugs. 2015 Jul;29(7):605-13. doi: 10.1007/s40263-015-0258-7. CNS Drugs. 2015. PMID: 26175116 Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of shortening time on diagnosis of 18F-florbetaben PET.EJNMMI Res. 2024 Nov 21;14(1):114. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01181-8. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 39570447 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics-Based Artificial Intelligence Differentiation of Neurodegenerative Diseases with Reference to the Volumetry.Life (Basel). 2022 Mar 31;12(4):514. doi: 10.3390/life12040514. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455005 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
- 2019YFC0118900/National Key Research and Development Program of China
- 61927801/National R&D Program for Major Research Instruments of Natural Science Foundation of China
- 62027808/National R&D Program for Major Research Instruments of Natural Science Foundation of China
- PGR00846/MAECI Great Relevance 2019 contributions Italy-China
- 689209/PICASO
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

