Vessel network extraction and analysis of mouse pulmonary vasculature via X-ray micro-computed tomographic imaging
- PMID: 33878108
- PMCID: PMC8594947
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008930
Vessel network extraction and analysis of mouse pulmonary vasculature via X-ray micro-computed tomographic imaging
Abstract
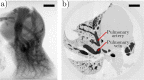
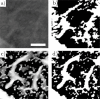
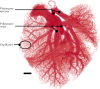
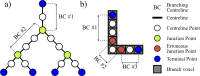
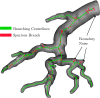
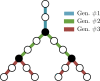
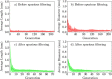
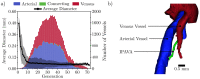
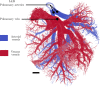
In this work, non-invasive high-spatial resolution three-dimensional (3D) X-ray micro-computed tomography (μCT) of healthy mouse lung vasculature is performed. Methodologies are presented for filtering, segmenting, and skeletonizing the collected 3D images. Novel methods for the removal of spurious branch artefacts from the skeletonized 3D image are introduced, and these novel methods involve a combination of distance transform gradients, diameter-length ratios, and the fast marching method (FMM). These new techniques of spurious branch removal result in the consistent removal of spurious branches without compromising the connectivity of the pulmonary circuit. Analysis of the filtered, skeletonized, and segmented 3D images is performed using a newly developed Vessel Network Extraction algorithm to fully characterize the morphology of the mouse pulmonary circuit. The removal of spurious branches from the skeletonized image results in an accurate representation of the pulmonary circuit with significantly less variability in vessel diameter and vessel length in each generation. The branching morphology of a full pulmonary circuit is characterized by the mean diameter per generation and number of vessels per generation. The methods presented in this paper lead to a significant improvement in the characterization of 3D vasculature imaging, allow for automatic separation of arteries and veins, and for the characterization of generations containing capillaries and intrapulmonary arteriovenous anastomoses (IPAVA).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Validation of the Gatortail method for accurate sizing of pulmonary vessels from 3D medical images.Med Phys. 2017 Dec;44(12):6314-6328. doi: 10.1002/mp.12580. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Med Phys. 2017. PMID: 28905390
-
Airway and pulmonary vascular measurements using contrast-enhanced micro-CT in rodents.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013 Jun 15;304(12):L831-43. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00281.2012. Epub 2013 Apr 5. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23564512
-
Segmentation and suppression of pulmonary vessels in low-dose chest CT scans.Med Phys. 2019 Aug;46(8):3603-3614. doi: 10.1002/mp.13648. Epub 2019 Jun 26. Med Phys. 2019. PMID: 31240721
-
Micro-computed tomography of the lungs and pulmonary-vascular system.Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005;2(6):477-80, 501. doi: 10.1513/pats.200508-080DS. Proc Am Thorac Soc. 2005. PMID: 16352751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactive three-dimensional volume rendering of spiral CT data: current applications in the thorax.Radiographics. 1998 Jan-Feb;18(1):165-87. doi: 10.1148/radiographics.18.1.9460115. Radiographics. 1998. PMID: 9460115 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of pulmonary artery variation based on 3D reconstruction of CT angiography.Front Physiol. 2023 Apr 27;14:1156513. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1156513. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37234424 Free PMC article.
-
Stereology and three-dimensional reconstructions to analyze the pulmonary vasculature.Histochem Cell Biol. 2021 Aug;156(2):83-93. doi: 10.1007/s00418-021-02013-9. Epub 2021 Jul 16. Histochem Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34272602 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microcomputed tomography visualization and quantitation of the pulmonary arterial microvascular tree in mouse models of chronic lung disease.Pulm Circ. 2023 Aug 27;13(3):e12279. doi: 10.1002/pul2.12279. eCollection 2023 Jul. Pulm Circ. 2023. PMID: 37645586 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative Imaging Metrics for the Assessment of Pulmonary Pathophysiology: An Official American Thoracic Society and Fleischner Society Joint Workshop Report.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023 Feb;20(2):161-195. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.202211-915ST. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2023. PMID: 36723475 Free PMC article.
-
Orthotopic transplantation of the bioengineered lung using a mouse-scale perfusion-based bioreactor and human primary endothelial cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Apr 4;14(1):7040. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-57084-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38575597 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forum of International Respiratory Societies. The Global Impact of Respiratory Disease–Second Edition. 2017.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

